|
Key Takeaways:
|
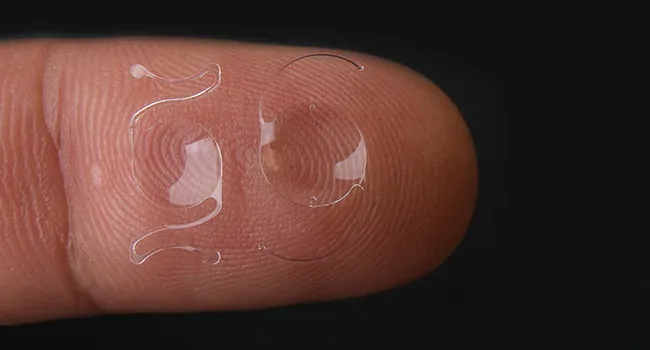
Cataract surgery is a well-established procedure that helps restore clear vision by replacing the clouded natural lens with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). The choice of lens plays a critical role in the quality of vision after cataract surgery, making it an important decision for every patient. Understanding the different types of cataract lenses can help patients make informed choices based on their specific vision needs.
This article explores the various IOL options available, including monofocal, multifocal and toric lenses, along with key considerations for selecting the most suitable lens.
What Are Cataract Lenses?
Cataract lenses, or intraocular lenses (IOLs), are artificial lenses implanted in the eye during cataract procedures to replace the clouded natural lens. These lenses are designed to restore vision and may offer varying levels of focus, depending on the type chosen.
Cataract lenses are primarily categorised based on their focusing ability:
- Monofocal lenses provide a single focus point, usually for distance vision.
- Multifocal lenses offer multiple focus points, enabling both near and distance vision.
- Toric lenses correct astigmatism in addition to addressing cataracts.
Each type of lens bears advantages and considerations, making it essential to understand its functionalities.
Monofocal Intraocular Lenses
Monofocal IOLs give one clear focus point; most people choose distance and use reading glasses for near tasks. They are reliable, clear, and the standard choice for many patients.
Benefits of Monofocal Lenses
- Clear, sharp vision at a chosen distance (usually far).
- Simple optics; fewer halos/glare than some premium lenses.
- The most affordable option; widely available.
Drawbacks of Monofocal Lenses
- Does not correct presbyopia (near focus); reading glasses are likely.
- Standard monofocal does not correct astigmatism (unless you choose a toric version).
- Depth of focus is narrow compared to multifocal/EDOF.
Cost of Monofocal Lenses in India
- Approx. ₹10,000–₹45,000 per eye for the lens tier used in surgery packages; varies by brand (Indian vs imported) and city.
Multifocal Intraocular Lenses
Multifocal IOLs have multiple focus zones to reduce the need for glasses for both distance and near (and some intermediate).
Benefits of Multifocal Lenses
- Greater freedom from glasses for many tasks (distance + near).
- Helpful for active lifestyles (reading on the go, phone use).
- Available in bi-/tri-focal designs to widen the range.
Drawbacks of Multifocal Lenses
- More halos/glare, especially at night, for some people.
- Adaptation period, brain and eyes learn the pattern.
- Not ideal if you need precision night vision.
Cost of Multifocal Lenses in India
- Approx. ₹45,000–₹95,000+ per eye depending on brand (Indian/imported) and model.
Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) Lenses
EDOF IOLs offer a continuous range of focus, typically distance + intermediate (for computer use), with some near vision; many people still use light readers for fine print.
Benefits of Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) Lenses
- Smooth distance-to-intermediate vision (driving + computer).
- Fewer halos than some multifocals.
- Good option if you want less glasses but do lots of mid-range work.
Drawback of Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) Lenses
- Fine print may still need glasses.
- Suitability depends on cornea/retina health and measurements.
- Costs more than standard monofocal.
Cost of Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) Lenses in India
- Approx. ₹70,000–₹1,40,000+ per eye, brand and city dependent (e.g., Vivity, Symfony-type EDOF).
Toric Intraocular Lenses
Toric lenses are designed to correct astigmatism (an uneven corneal curve) at the same time as cataract removal. You can get toric monofocal or toric multifocal/EDOF versions.
Benefits of Toric Lenses
- Sharper distance by correcting astigmatism inside the eye.
- Can be combined with multifocal/EDOF designs for a broader range.
- More stable astigmatism correction than glasses for many patients.
Drawback of Toric Lenses
- Needs precise alignment; rotation can blur vision.
- Surgery Costs more than non-toric versions.
- Very irregular corneas may not suit toric optics.
Cost of Toric Lenses in India
- Approx. ₹30,000–₹1,20,000+ per eye for toric IOLs; advanced toric multifocal/EDOF options can be higher.
Monofocal vs Multifocal IOLs
If you want clear distance and don’t mind using reading glasses, a monofocal IOL is a great, lower-cost choice. If your goal is less dependence on glasses for most activities and you’re okay with a possible adaptation period (and some halos/glare at night), a multifocal IOL may suit you better.
Your surgeon will match the choice to your eyes, lifestyle, night-vision needs, and budget.
|
Feature |
Monofocal IOL |
Multifocal IOL |
|
Focus range |
One clear focus (usually distance). |
Several focus points (distance + near, often intermediate too). |
|
Glasses use |
Reading glasses are likely for near tasks |
Less need for glasses for most daily tasks; fine print may still need weak readers. |
|
Night vision |
Generally clean night vision. |
Some people notice halos/glare around lights at night. |
|
Contrast clarity |
Often crisp contrast (especially in low light). |
Contrast can be slightly reduced for some users. |
|
Adaptation time |
Little to no adaptation. |
Adaptation period common; brain learns multiple focus zones. |
|
Computer/phone use |
May need readers or set one eye for near (mini-monovision). |
Usually good for a phone/computer without glasses |
|
Astigmatism option |
Toric monofocal can correct astigmatism. |
Toric multifocal/EDOF versions exist (selection is stricter). |
|
Cost |
Lower (standard option in many packages). |
Higher (premium technology). |
|
Best for |
Drivers, night workers, people who want simple optics |
People who want less dependence on glasses and accept small trade-offs. |
|
Not ideal if |
You want glasses-free near vision. |
You need perfect night vision or have eye issues that reduce quality (doctor decides). |
|
Customization |
Can do mini-monovision (one eye set slightly nearer). |
Many designs (bi/tri-focal, EDOF-like), fit depends on your eyes and goals. |
Patients prioritising clear distance vision without visual artefacts may prefer monofocal lenses, while those desiring reduced dependence on glasses may opt for multifocal options.
Choosing the Best Lens for Cataract Surgery
Selecting the right IOL depends on several factors:
- Lifestyle Needs: Active individuals may prefer multifocal lenses, while those prioritising precise night vision may choose monofocal options.
- Budget Considerations: Monofocal lenses are often covered by insurance, whereas premium lenses may require out-of-pocket costs.
- Pre-existing Eye Conditions: Patients with astigmatism benefit from toric lenses, while those with presbyopia may prefer multifocal IOLs.
A consultation with an ophthalmologist is essential to determine the most suitable lens based on individual needs.
Procedure and Recovery
Cataract surgery is an outpatient procedure that typically lasts 15 to 30 minutes per eye. The steps include:
- Application of local anaesthesia and dilation of the pupil.
- Removal of the clouded lens using ultrasound or laser-assisted techniques.
- Implantation of the selected IOL.
- Post-operative care to monitor healing and optimise results.
Recovery usually takes a few weeks, during which patients should follow prescribed eye care routines and avoid strenuous activities.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of cataract lenses is essential for making an informed decision about vision correction. Factors such as lifestyle, pre-existing conditions, and budget play a crucial role in selecting the right IOL. Consulting an eye specialist can help patients determine the most suitable option based on their unique needs.
Take the first step toward clearer vision! Consult with an eye specialist.
FAQs
Intraocular lenses (IOLs) are typically made of biocompatible materials such as silicone or acrylic. These materials are chosen for their durability, optical clarity, and ability to safely remain within the eye after cataract surgery.
The choice of the best lens for cataract surgery depends on individual needs. Monofocal lenses offer reliable results, while multifocal or extended depth of focus lenses may reduce dependence on glasses for various distances, but can have visual disturbances.
Monofocal IOLs are generally the most affordable type of cataract lenses.
In Monofocal vs Multifocal lens, Monofocal lenses provide clear vision at one distance, requiring glasses for other ranges, while multifocal lenses offer a broader range of vision but may come with increased risk of visual disturbances like halos and glare. The choice depends on individual preferences and lifestyle considerations.
Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) lenses are among the latest types of lenses for cataract surgery, aimed to provide a continuous range of vision, reducing the need for glasses across various distances.
Monofocal lenses provide reliable vision at one distance, while multifocal or extended depth of focus lenses offer a broader range, reducing the need for glasses. Consultation with an ophthalmologist helps determine the best fit based on individual preferences and lifestyle.
In cataract surgery, an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) replaces the clouded natural lens and helps light focus onto the retina, enabling patients to see clearly at specific distances, depending on the type of lens chosen.
The clarity of vision depends on individual eye health and lifestyle needs. Monofocal lenses offer sharp distance vision, while multifocal lenses provide a broader range of focus.
Cataract lenses are designed to be permanent and do not degrade over time. They typically last a lifetime without needing replacement.
Yes, toric lenses are specifically designed to correct astigmatism while addressing cataracts.
No, cataract surgery is performed under local anaesthesia, ensuring a painless experience. Mild discomfort may be present during the recovery phase.