Glaucoma is a progressive eye condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. It is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” because it can develop without noticeable symptoms in the early stages. As the disease progresses, it can cause irreversible damage to the optic nerve, leading to permanent blindness. Understanding the symptoms of glaucoma and adopting preventive measures can help maintain good eye health and slow the progression of the condition.
What is Glaucoma?
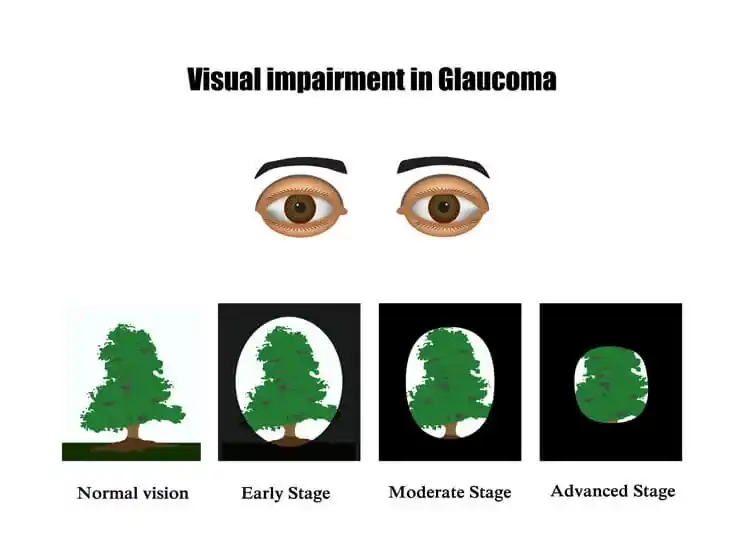
Glaucoma is a group of eye disorders that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eyes to the brain, making it essential for clear vision. When pressure inside the eye builds up, it can compress and damage the nerve fibers, resulting in gradual vision loss.
There are different types of glaucoma, including:
- Open-angle glaucoma: The most common type, characterized by slow and progressive vision loss.
- Angle-closure glaucoma: A more severe form that occurs suddenly and requires immediate medical attention.
- Normal-tension glaucoma: Occurs despite normal eye pressure levels, making it difficult to detect early.
- Congenital glaucoma: Present at birth due to abnormal eye development.
Understanding these types is crucial in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment.
Causes of Glaucoma
Glaucoma occurs due to improper drainage of aqueous humor, the fluid inside the eye. This leads to increased pressure, which damages the optic nerve. Some underlying causes include:
- Blocked drainage channels: When the eye’s drainage system becomes clogged, fluid accumulates, increasing eye pressure.
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of glaucoma increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Eye injuries or trauma: Physical damage to the eye can interfere with fluid drainage and lead to elevated pressure.
- Underlying health conditions: Diseases such as diabetes and hypertension can contribute to optic nerve damage.
- Prolonged corticosteroid use: Long-term use of steroid medications, especially eye drops, can raise intraocular pressure.
Risk Factors of Glaucoma
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of developing glaucoma. These risk factors include:
- Family history of glaucoma: If immediate family members have glaucoma, the risk is significantly higher.
- Age: People over 40 are at greater risk, with the likelihood increasing as they age.
- High blood pressure and diabetes: These conditions can compromise blood flow to the optic nerve.
- Thin corneas: A thinner-than-average cornea may indicate a higher susceptibility to glaucoma.
- Prolonged exposure to screen time: Straining the eyes for long hours may increase intraocular pressure over time.
Main Symptoms of Glaucoma
The main symptoms of glaucoma vary based on the type and stage of the disease. Some symptoms are subtle and go unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. Common symptoms include:
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision: One of the earliest signs, often starting with blind spots at the edges of vision.
- Blurry or hazy vision: A general decrease in visual clarity, making reading or focusing difficult.
- Eye pain or discomfort: A dull or sharp pain in the eyes, more common in acute cases like angle-closure glaucoma.
- Halos around lights: Seeing rainbow-colored rings around light sources, especially in dim environments.
- Frequent changes in prescription: Needing new glasses or contact lenses more frequently due to fluctuating vision.
- Redness and irritation: Eyes may appear bloodshot and feel irritated due to increased pressure.
- Sudden vision loss: In severe cases, a rapid and dramatic loss of vision can occur, requiring immediate medical intervention.
What Are Early Signs of Glaucoma?
In many cases, glaucoma does not present noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, some early signs to watch for include:
- Difficulty adjusting to dim lighting: Trouble seeing in low-light conditions, such as at night or in dark rooms.
- Mild headaches or eye strain: Unexplained discomfort around the eyes, often mistaken for general fatigue.
- Frequent need to rub eyes: Increased pressure in the eyes may lead to an urge to massage or rub them.
- Reduced contrast sensitivity: Difficulty distinguishing between similar colors or detecting small changes in brightness.
- Tunnel vision: The field of view narrows, making it challenging to see objects at the sides.
Recognizing what are early signs of glaucoma is essential for seeking timely intervention and preventing further progression of the disease.
Read about Remedies and Techniques to Prevent Glaucoma.
Symptoms of Glaucoma in Men
Men may experience faster progression of glaucoma symptoms due to lifestyle factors such as smoking, stress, and occupational exposure to eye strain. Some symptoms include:
- Increased eye strain from prolonged screen time.
- Higher susceptibility to optic nerve damage due to hypertension.
- Frequent dryness or irritation due to environmental exposure.
Being aware of symptoms of glaucoma in men can help in early diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing vision loss.
Symptoms of Glaucoma in Women
Women with glaucoma may face additional challenges due to hormonal changes and higher life expectancy. Common symptoms include:
- Dry eyes and discomfort, especially post-menopause.
- Sensitivity to bright lights and glare.
- Increased intraocular pressure during pregnancy.
Early detection of symptoms of glaucoma in women can aid in better management of the condition.
Symptoms of Glaucoma in Young Adults
Glaucoma is less common in young adults but can still occur, particularly in those with genetic predisposition. Symptoms may include:
- Persistent eye strain after reading or using digital devices.
- Mild but consistent headaches.
- Occasional blurry vision, especially in one eye.
Identifying symptoms of glaucoma in young adults is crucial as early treatment can help in preserving vision over time.
Preventive Tips for Glaucoma
While glaucoma cannot always be prevented, certain measures can help reduce the risk:
- Regular eye exams to detect early signs.
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E.
- Controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Avoiding excessive screen time and eye strain.
Exercises for Eye Health for Glaucoma
Certain eye exercises may help improve circulation and relieve pressure:
- Palming: Rubbing the hands together and placing them over the eyes to relax eye muscles.
- Blinking exercises: Blinking rapidly for a few seconds to improve tear production.
- Focus shifting: Alternating focus between near and distant objects to strengthen eye muscles.
Lifestyle Changes to Avoid Glaucoma
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage glaucoma risk. Recommended changes include:
- Staying hydrated to maintain eye fluid balance.
- Reducing caffeine intake to avoid pressure spikes.
- Engaging in regular physical activity to promote circulation.
- Wearing protective eyewear to prevent eye injuries.
Don’t wait for symptoms to progress—schedule a comprehensive eye check-up today! Book an Eye Exam Now
FAQs
Early signs include mild eye discomfort, difficulty adjusting to dim lighting, occasional blurriness, and gradual peripheral vision loss.
In cases like acute angle-closure glaucoma, vision loss can occur suddenly, accompanied by severe eye pain and nausea.
While symptoms are generally similar, women may experience increased eye dryness and discomfort due to hormonal changes, while men might have a higher risk of optic nerve damage due to lifestyle factors.
Yes, symptoms of glaucoma in young adults may include persistent eye strain, mild headaches, and difficulty focusing, which can be mistaken for routine eye fatigue.
If you notice blurred vision, frequent headaches, halos around lights, or peripheral vision loss, schedule an eye exam immediately to prevent potential complications.