Introduction: Welcome to our comprehensive blog on Rosette Cataract, a unique and intriguing form of cataract that captivates the attention of both ophthalmologists and patients alike. Characterized by its distinctive rosette shaped cataractous opacities within the crystalline lens, Rosette Cataract stands out among various types of cataracts due to its specific appearance and potential impact on vision. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of Rosette Cataract, exploring its causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking a deeper understanding or an individual facing the challenges of Rosette Cataract, this guide aims to provide valuable insights to help navigate through the complexities of this eye condition.
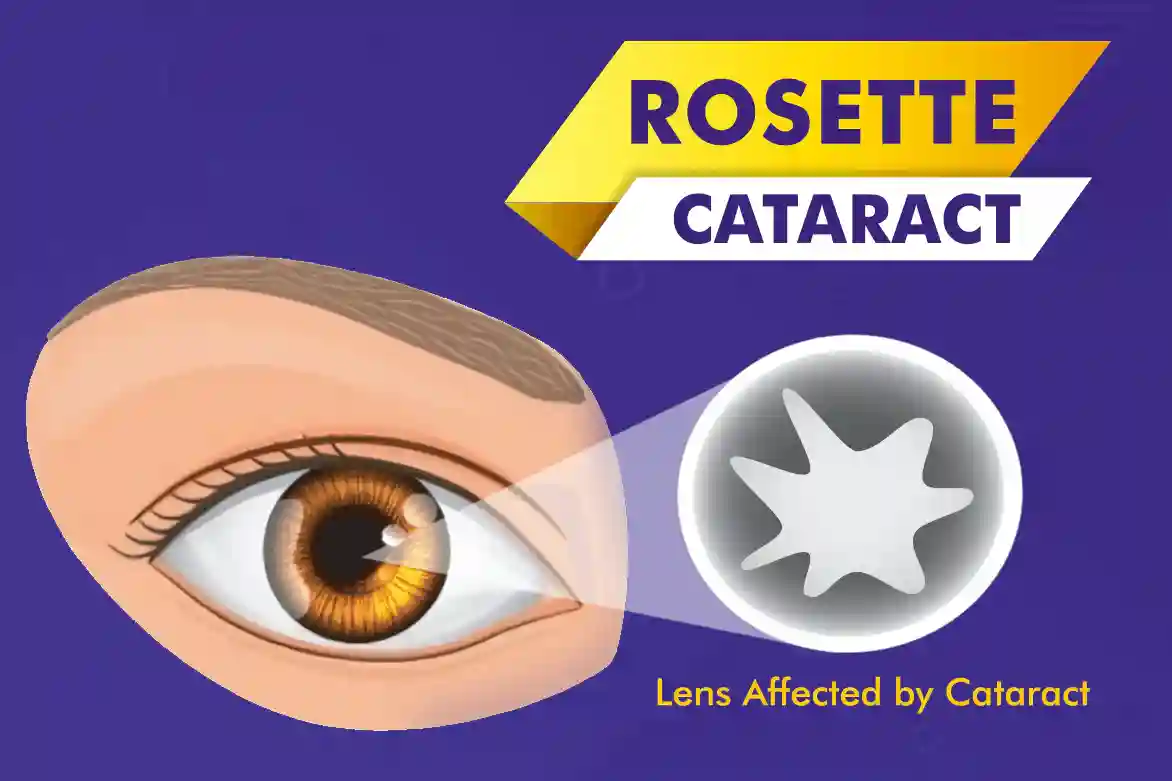
What Is Rosette Cataract?
Rosette cataract is a specific type of cataract that affects the eye’s lens. It is characterized by the formation of rosette shaped cataractous opacities in the lens, which can interfere with vision. These opacities appear as concentric circles and can vary in size and density. This type of cataract is relatively rare and may be present at birth or develop later in life. It can affect one or both eyes.
The exact cause of rosette cataract is not fully understood, but it is believed to be caused by genetic mutations that affect the development and structure of the lens. In some cases, it may be associated with other genetic disorders or syndromes. Rosette cataract cause can have a significant impact on vision, depending on the size and location of the opacities. It can cause blurred or distorted vision, difficulty seeing in low light conditions, and increased sensitivity to glare.
Treatment for rosette cataract typically involves surgical removal of the affected lens and replacement with an artificial lens. This can help restore vision and improve overall visual function.
Rosette Cataract Symptoms
The symptoms of rosette cataract can vary depending on the size and location of the opacities in the lens. Some common symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light conditions
- Increased sensitivity to glare
- Reduced visual acuity
- Poor night vision
It is important to note that not all individuals with rosette cataract will experience the same symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary. If you experience any changes in your vision or suspect you may have rosette cataract, it is important to consult with an eye care professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Rosette Cataract
The exact causes of rosette cataract are not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. Some possible causes include:
- Blunt Force Trauma to the Head:
Rosette cataract cause can be triggered by a significant impact or injury to the head, leading to damage within the crystalline lens and the formation of characteristic rosette shaped cataractous opacities.
- Ocular Trauma to the Eyeball:
Direct trauma to the eyeball, whether through accidents or injuries, can induce Rosette Cataract, causing structural changes in the lens and affecting vision.
- Exposure to Radiation:
Prolonged exposure to certain types of radiation, such as ionizing radiation, has been associated with the development of Rosette Cataract, highlighting the importance of protective measures in radiation-related environments.
- Subconjunctival Hemorrhage or Eye-Bleeding:
Instances of subconjunctival hemorrhage, where blood pools beneath the conjunctiva, may contribute to the formation of rosette opacities in the crystalline lens, linking eye bleeding to the development of this unique cataract.
- Electrocution:
Electrical injuries, including electrocution, can lead to Rosette Cataract, emphasizing the importance of electrical safety measures to prevent potential eye damage.
- Chemical Burns:
Exposure to corrosive chemicals or substances can result in chemical burns to the eye, potentially causing the formation of rosette shaped cataractous opacities within the lens and impacting visual function.
It is important to note that not all cases of rosette cataract have a known cause, and some may be attributed to genetic mutations or other underlying conditions.
How Does It Impact Everyday Life?
Rosette cataract can have a significant impact on everyday life. The visual disturbances caused by the opacities in the lens can make it difficult to perform daily activities that require clear vision, such as reading, driving, or recognizing faces.
Additionally, the increased sensitivity to glare and reduced visual acuity can make it challenging to navigate in bright or low light conditions. This can affect the individual’s independence and overall quality of life.
However, with appropriate diagnosis and treatment, many individuals with rosette cataract can experience significant improvement in their vision and regain their ability to perform daily activities.
Types of Rosette Cataract
There are several types of rosette cataract, including:
- Anterior polar rosette cataract: characterized by opacities in the front portion of the lens
- Posterior polar rosette cataract: characterized by opacities in the back portion of the lens
- Lamellar rosette cataract: characterized by opacities in the middle layer of the lens
- Total rosette cataract: characterized by opacities throughout the entire lens
The specific type of rosette cataract can impact the severity of symptoms and the recommended treatment approach.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing rosette cataract typically involves a comprehensive eye examination, including a visual acuity test, slit-lamp examination, and dilated eye examination. Additional tests, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or ultrasound, may be performed to assess the size and location of the opacities.
The mainstay of treatment for rosette cataract is surgery. The affected lens is surgically removed and replaced with an artificial lens, known as an intraocular lens (IOL). This procedure is called cataract surgery and is typically performed on an outpatient basis.
Cataract surgery is generally safe and has a high success rate in improving vision. After surgery, the individual may be prescribed eye drops or other medications to prevent infection and promote healing.
It is important to follow all post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon and attend follow-up appointments for monitoring and evaluation of the surgical outcomes.
Read more about –Types of cataract treatment
Tips To Prevent Rosette Cataract
Since the exact causes of rosette cataract are not fully understood, there are no specific preventive measures that can be taken to avoid its development. However, there are general steps individuals can take to maintain good eye health and reduce the risk of cataracts in general.
- Protect the eyes from injury by wearing appropriate eye protection during sports or other activities that pose a risk of eye trauma.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Quit smoking, as smoking has been linked to an increased risk of cataract development.
- Manage underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, as uncontrolled diabetes can contribute to cataract formation.
Regular eye examinations are also important for early detection and treatment of any eye conditions, including rosette cataract. It is recommended to have a comprehensive eye examination at least once every two years, or as advised by an eye care professional.
Conclusion: This guide has explored the nuances of Rosette Cataract, providing a comprehensive overview for both medical professionals and individuals dealing with this unique eye condition. From its distinctive features to diagnostic insights and treatment options, our aim is to empower readers with valuable knowledge. Staying informed and collaborating with healthcare professionals remains essential for personalized care. By fostering awareness and understanding, we contribute to improving the management and outcomes of Rosette Cataract, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this ocular challenge.
FAQs
Can rosette cataract be inherited?
Yes, rosette cataract can be inherited. It is often caused by genetic mutations that affect the development and structure of the lens. If a family member has rosette cataract, there may be an increased risk of developing the condition.
Can rosette cataract be treated with medication?
No, rosette cataract cannot be treated with medication. The main treatment option is surgical removal of the affected lens and replacement with an artificial lens.
Is rosette cataract reversible?
Rosette cataract is typically not reversible. Once the opacities form in the lens, they cannot be removed without surgical intervention.
Can rosette cataract cause blindness?
Untreated rosette cataract can significantly impact vision and may lead to blindness if left untreated. However, with appropriate diagnosis and treatment, vision can be restored and the risk of blindness can be minimized.
Is rosette cataract common?
Rosette cataract is relatively rare compared to other types of cataract. Its prevalence may vary depending on the population studied and other factors. It is important to consult with an eye care professional for personalized information and advice regarding rosette cataract.
What is the difference between early and late rosette cataracts?
Early rosette cataracts have a star-shaped pattern, while late rosette cataracts show more complex formations.
What is rosette cataract?
Rosette cataracts are characterized by a flower-like pattern in the lens.