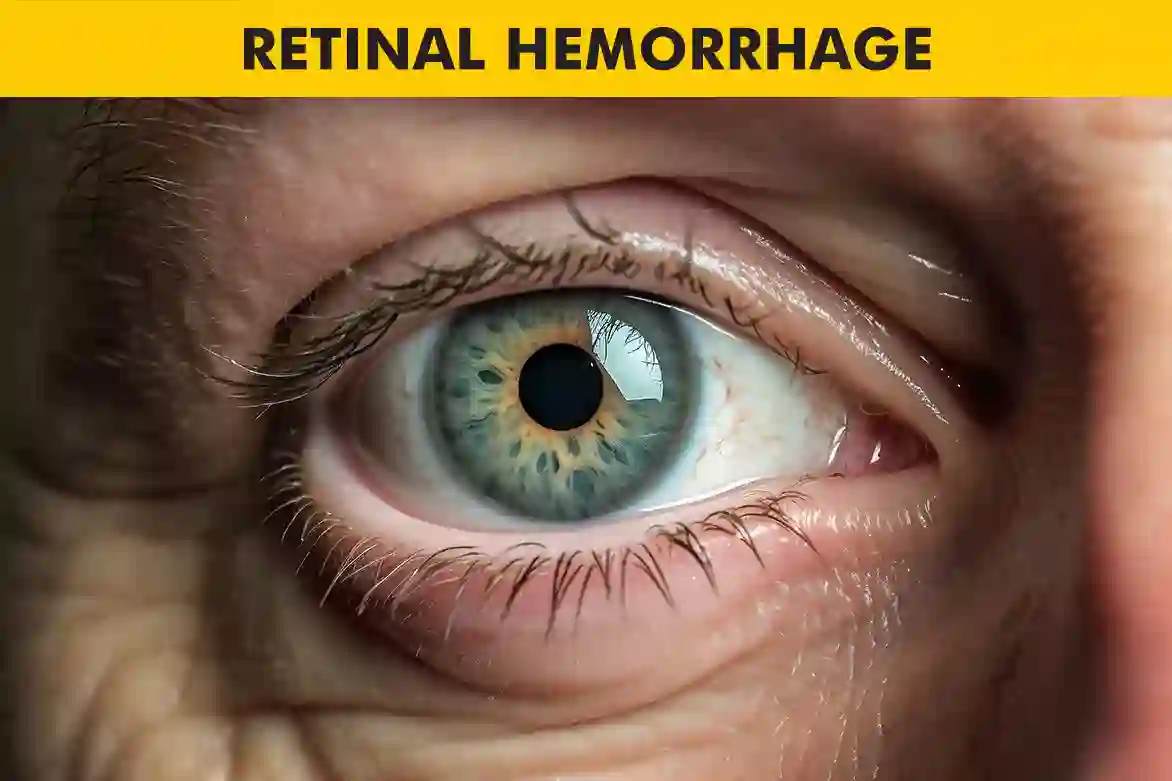
Retinal hemorrhage or retinal bleeding, a condition characterized by bleeding in the delicate tissue of the retina, is a serious concern that necessitates immediate medical attention. Various factors can lead to retinal hemorrhage, ranging from physical trauma to underlying health conditions and even certain medications. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention are crucial steps in preventing further harm to the eye and preserving vision.
Understanding the complexities of retinal hemorrhage involves grasping the intricate anatomy of the eye and how retinal bleeding can impact visual health. This blog aims to delve deeper into the signs, reasons, and treatment possibilities associated with hemorrhage of the retina.
What Is Retinal Hemorrhage or Retinal Bleeding?
Retinal hemorrhage is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on vision and overall eye health. Understanding the anatomy of the eye is crucial in grasping how this bleeding occurs and the potential consequences it can have. The retina, a delicate layer of tissue at the back of the eye, plays a vital role in capturing light and transmitting visual signals to the brain. When the blood vessels within the retina become damaged or compromised, it can lead to retinal hemorrhage.
This bleeding can manifest in various ways, causing symptoms such as blurred vision, floaters, or even loss of vision in certain areas. It is essential to recognize these signs and seek prompt medical attention to address the underlying issue and prevent further damage to the eye. By understanding the mechanisms behind retinal hemorrhage and being aware of the potential symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their vision and overall eye health.
Types of Retinal Hemorrhage
Subhyaloid hemorrhage: This type of retinal hemorrhage occurs between the retina and the vitreous humor, which is the gel-like substance that fills the eye. Subhyaloid hemorrhages are often associated with conditions such as diabetic retinopathy or retinal vein occlusion, and they can indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed promptly.
Preretinal hemorrhage: Preretinal hemorrhages occur between the retina and the inner surface of the eye, known as the hyaloid membrane. These types of hemorrhages can be caused by trauma, high blood pressure, or blood clotting disorders. Identifying a preretinal hemorrhage can help healthcare professionals pinpoint the source of the retinal bleeding and determine the most effective course of treatment.
Intraretinal hemorrhage: Intraretinal hemorrhages occur within the layers of the retina itself, often as a result of conditions like age-related macular degeneration or retinal vascular diseases. These hemorrhages can vary in severity and may require different approaches to treatment depending on the underlying cause. Understanding the specific location of the hemorrhage within the retina is crucial in devising a targeted treatment of retinal hemorrhage for the patient.
Vitreous hemorrhages: Bleeding inside the vitreous humor leads to Vitreous hemorrhages. It generally occurs due to the general disorders of the eye’s structures as well as some diseases that affect the body.
Each type of hemorrhage offers valuable insights into the underlying health conditions or factors contributing to the bleeding, guiding the path towards effective treatment and management strategies.
Symptoms of Retinal Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage of retina can cause painless, near-complete loss of vision. This happens if there is enough blood to make the vitreous opaque. You may only be able to make out light and dark. Lesser amounts of hemorrhage can cause
- Blurred vision
- Dark spots
- Cobwebs
- Haze
- Shadows
- Floaters.
The vision loss is often worse in the morning because the blood has settled at the back of the eye. This covers the macula, the part of the retina that gives the sharpest vision.
Common Causes of Retinal Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage of retina can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Trauma to the eye or head
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Blood clotting disorders
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Retinal vein occlusion
- Certain medications, such as blood thinners
- Eye surgery
Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for the appropriate treatment of retinal hemorrhage and the prevention of future occurrences.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If retinal bleeding is suspected, a comprehensive eye examination will be conducted by an eye care professional. This may include:
- Visual acuity test
- Retinal examination
- Fluorescein angiography
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
In some cases, the retinal bleeding may resolve on its own without any intervention. However, if necessary, treatment of retinal hemorrhage options may include laser therapy, vitrectomy, or medication to manage the underlying condition.
Prevention and Long-term Management
While it may not always be possible to prevent retinal hemorrhage, there are certain measures that can help reduce the risk or manage the condition effectively:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Control underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Avoid trauma to the head and eyes
- Follow proper safety precautions during activities that may pose a risk to the eyes
Long-term management of retinal hemorrhage may involve regular follow-up appointments with an eye care professional to monitor the condition and ensure timely intervention if needed.
Conclusion
Retinal hemorrhage, a condition characterized by bleeding in the delicate tissue of the retina, is a serious concern that necessitates immediate medical attention. Understanding the complexities of retinal hemorrhage involves grasping the intricate anatomy of the eye and how bleeding in the retina can impact visual health. The retina, positioned at the back of the eye, plays a pivotal role in capturing light and transmitting visual signals to the brain. When the blood vessels within the retina sustain damage or compromise, it can result in retinal hemorrhage.
You may explore Retina and Uvea Services offered by the Centre For Sight Eye Experts.
FAQs
What can cause retinal hemorrhage?
Retinal hemorrhage can be caused by hypertension, diabetes, trauma, or blood disorders.
What causes a hemorrhage in the eye?
Eye hemorrhages can be caused by trauma, hypertension, diabetes, or certain medications.
How long does a retinal bleeding take to clear?
The time for a retinal bleeding to clear can vary, but it typically resolves within a few weeks to months.
What will show retinal hemorrhages?
Retinal hemorrhages can be detected during a dilated eye examination by an ophthalmologist or optometrist.
Can retinal hemorrhage be repaired?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause; some cases may resolve on their own, while others may require medical intervention.
Can stress cause retinal hemorrhage?
Extreme stress alone is unlikely to cause retinal hemorrhage; it is usually due to underlying medical conditions.
Can eye hemorrhage be cured?
Yes, depending on the cause, eye hemorrhages can often be treated and resolved, especially with appropriate medical care.