Eyes, the windows to our world, play a crucial role in our daily lives. However, just like any other part of our body, they too can face challenges. One such challenge is the development of posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC), a condition that can cloud our vision and impact our daily activities.
In this blog, we will embark on a journey to demystify PSC cataract, exploring its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and delving into the available posterior subcapsular treatment options. Whether you’re seeking information for yourself or a loved one, understanding Posterior Subcapsular Cataract is a vital step towards maintaining clear vision and a higher quality of life. Let’s navigate through the intricacies of this eye condition together, shedding light on the path to better eye health.
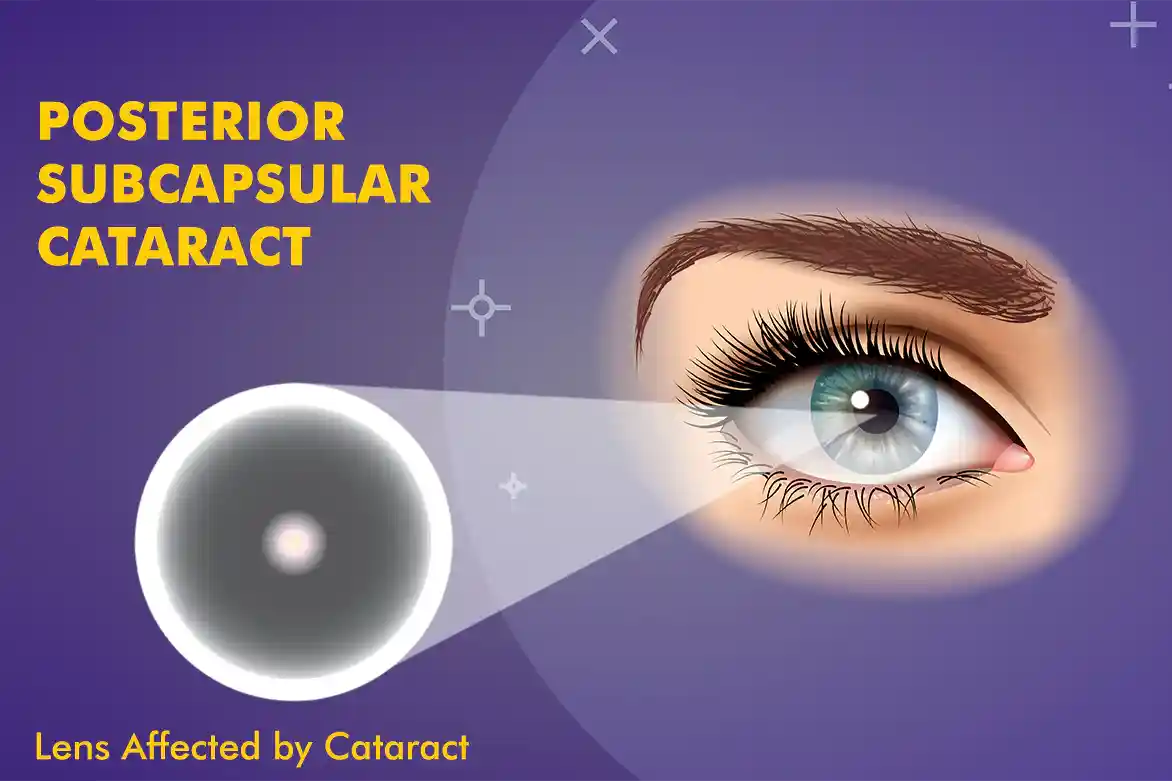
What Is Posterior Subcapsular Cataract?
Posterior subcapsular cataract is a specific type of cataract that affects the lens of the eye. The lens, located behind the iris (colored part of the eye), helps focus light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. A cataract occurs when the lens becomes cloudy, impairing vision. In the case of PSC cataract, the cloudiness specifically develops in the back part of the lens capsule, which is the outer covering of the lens. This can result in difficulties with tasks like reading, seeing in bright light, or dealing with glare. It is often associated with aging, but certain factors like prolonged steroid use, diabetes, and eye trauma can also contribute to its development.
Understanding the nature of posterior subcapsular cataract is essential for recognizing its symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment to maintain good eye health.
Symptoms of Posterior Subcapsular Cataract
Recognizing the symptoms of posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC) is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Individuals with it may experience the following symptoms:
Blurred Vision:
Blurriness, especially in the central part of the vision, is a common symptom of PSC cataract. This can make activities like reading or focusing on fine details challenging.
Glare Sensitivity:
Increased sensitivity to glare, particularly in bright light conditions, is often reported by individuals. Headlights, sunlight, or other bright lights may cause discomfort and difficulty seeing clearly.
Difficulty with Night Vision:
Night vision gets impacted, making it harder to see in low-light environments. This may lead to challenges while driving at night or navigating dimly lit spaces.
Halo Effect:
Some individuals with posterior subcapsular cataract may experience the perception of halos around lights, adding to the difficulty of seeing clearly, especially in low-light situations.
Reduced Contrast Sensitivity:
PSC cataract can decrease the ability to distinguish between objects of similar colors or shades, making it challenging to perceive contrasts in the surrounding environment.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can develop gradually, and individuals experiencing any changes in their vision should promptly consult with an eye care professional.
Also read about Types of cataract treatment
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Causes
The development of PSC cataract is influenced by various factors. While aging is a primary cause, there are other contributing factors that can increase its risks. Here are some common causes:
Aging:
The natural aging process is a significant contributor to the formation of cataracts, including posterior subcapsular cataracts. Over time, changes in the lens structure occur, leading to cloudiness and impaired vision.
Steroid Use:
Prolonged and systemic use of corticosteroid medications, whether oral, topical, or inhaled, can elevate the risk of developing it.
Diabetes:
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing various eye conditions, including PSC cataract too. High blood sugar levels can contribute to changes in the lens and accelerate the formation of cataracts.
Trauma to the Eye:
Physical injury or trauma to the eye can increase the likelihood of developing posterior subcapsular cataracts. Injury may disrupt the normal structure of the lens and contribute to the formation of cataracts.
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation:
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation, especially without proper eye protection, is associated with an increased risk of developing cataracts. Sunglasses that block UV rays can help reduce this risk.
Genetics:
Family history can play a role in the predisposition to cataracts. If close relatives have had cataracts, there may be a higher likelihood of developing them.
Understanding these causes can help individuals take proactive steps to minimize risk factors, such as protecting their eyes from UV rays, managing diabetes effectively, and using medications under proper medical supervision.
Also read about Congenital Cataract
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing posterior subcapsular cataracts, like:
- Age: The risk rises with age.
- Steroid Use: Prolonged use of corticosteroids increases susceptibility.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes can contribute to cataract formation.
- UV Radiation: Long-term exposure without eye protection raises the risk.
- Eye Trauma: Injury to the eye can elevate the risk.
- Genetics: Family history may increase susceptibility.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Both are linked to an increased risk.
- Certain Medications: Some medications may contribute to cataract development.
- Obesity: Being overweight is associated with a higher risk.
- Previous Eye Surgery: History of eye surgery or inflammation increases susceptibility.
Being aware of these factors can help individuals take preventive measures and prioritize eye health.
How Does Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Impacts vision
Posterior subcapsular cataract impacts vision by causing changes in the clarity of the lens, particularly in the back part of the lens capsule.
Blurred Vision: Central vision becomes blurry, impacting activities like reading.
Glare Sensitivity: Bright lights cause discomfort and reduce visual clarity.
Difficulty with Night Vision: PSC cataract can make seeing in low-light conditions, like driving at night, challenging.
Halo Effect: Some may see halos around lights, especially in low-light situations.
Reduced Contrast Sensitivity: This can lessen the ability to distinguish between similar colors or shades.
These vision changes occur gradually, and regular eye check-ups are crucial for early detection and effective management
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Diagnosis
Diagnosing posterior subcapsular cataract involves a comprehensive eye examination that includes the following steps:
Visual Acuity Test: Assessing clarity of vision at different distances.
Slit-Lamp Examination: Examining the eye structures under magnification.
Dilated Eye Examination: Enlarging the pupils for a thorough lens and eye assessment.
Tonometry: Measuring intraocular pressure to rule out other conditions.
Retinal Examination: Evaluating the health of the retina and optic nerve.
Based on the findings from these examinations, the eye care professional can determine the presence and extent of posterior subcapsular cataracts.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Prevention
While it’s not always possible to completely prevent the development of posterior subcapsular cataracts, there are lifestyle choices that can reduce the risk.
- UV Protection: Wear sunglasses to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins C and E.
- Regular Eye Exams: Schedule routine check-ups for early detection.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk, so quitting can be beneficial.
- Diabetes Management: Control blood sugar levels to lower the risk.
- Limit Alcohol: Moderating alcohol intake may reduce the risk.
- Protective Eyewear: Use eye protection during activities with injury potential.
- Manage Steroid Use: If on corticosteroids, work with healthcare providers to minimize the risk.
Consult with an eye care professional for personalized advice based on individual health and risk factors.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Treatment
The primary treatment for posterior subcapsular cataracts is surgical intervention.
Cataract Surgery:
Removes the cloudy lens, replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
IOL Types:
Various IOLs are available, addressing different vision needs.
Recovery:
Typically done one eye at a time, with improved vision shortly after posterior subcapsular cataract surgery and complete recovery in a few weeks.
Follow-up Care:
Regular check-ups with the eye surgeon are crucial for monitoring healing.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Prescription eyeglasses may be needed post posterior subcapsular cataract surgery, and the eye care professional guides on any necessary adjustments.
Read about Tips to prevent cataract
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract Treatment in India
Centre For Sight in India is a trusted destination for posterior subcapsular cataract treatment, offering advanced phacoemulsification surgery and a range of intraocular lenses. Known for skilled professionals and state-of-the-art facilities, it provides affordable and top-notch care, ensuring optimal healing and visual outcomes. Patients seeking reliable and personalized eye care can confidently consult with Centre For Sight, a renowned choice in India.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing posterior subcapsular cataracts are vital for optimal eye health. Whether through preventive measures like UV protection or advanced treatments like cataract surgery, early detection is key. Regular eye check-ups and informed decisions contribute to clear vision and overall well-being. A proactive approach empowers individuals to navigate the journey with confidence, preserving the precious gift of sight.
FAQs
What is the main causes for posterior subcapsular cataract?
Aging, prolonged steroid use, diabetes, and eye trauma are common causes of Posterior Subcapsular Cataract.
What are the common symptoms to watch for Posterior Subcapsular Cataract?
Watch for blurred vision, increased glare sensitivity, difficulty with night vision, halos around lights, and reduced contrast sensitivity.
How is Posterior Subcapsular Cataract diagnosed?
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination, including visual acuity tests and a dilated eye exam.
What treatment options are available for Posterior Subcapsular Cataract?
Posterior subcapsular cataract surgery, involving the removal of the cloudy lens and implantation of an intraocular lens, is the primary posterior treatment for Posterior Subcapsular Cataract.
What is the recovery process like after cataract surgery for posterior polar cataracts?
After cataract surgery, patients typically experience improved vision shortly and achieve complete recovery within a few weeks.
Are there any complications associated with cataract surgery for posterior polar cataracts?
While uncommon, risk of cataract surgery may include infection, bleeding, or changes in eye pressure.
Can posterior polar cataracts recur after cataract surgery?
Posterior polar cataracts generally do not recur after successful cataract surgery.
Can a posterior subcapsular cataract be fixed?
Yes, posterior subcapsular cataracts can be treated with surgery for visual improvement.
How fast do posterior subcapsular cataracts grow?
The growth rate of posterior subcapsular cataracts varies, but they tend to progress faster than other types.
Where is the posterior subcapsular area?
The posterior subcapsular area is the back part of the lens capsule, where these cataracts typically form.