Summary: Peripheral vision loss, also called tunnel vision, reduces side vision while central sight remains clear. It commonly occurs due to glaucoma, retinal diseases, stroke, diabetes, or brain injuries. Symptoms include bumping into objects, difficulty driving, and trouble seeing in low light. Early diagnosis, treatment, and vision rehabilitation help manage the condition and protect eyesight.
|
Key Takeaways:
|
Peripheral vision refers to seeing objects outside the direct line of sight without moving the eyes. It plays a crucial role in daily activities such as driving, walking, and playing sports, allowing individuals to detect motion and navigate their environment safely. Peripheral vision loss, also known as tunnel vision, occurs when an individual loses the ability to see objects on the sides while their central vision remains intact. This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making routine tasks more difficult and increasing the risk of accidents.
Peripheral vision loss can occur due to various eye and neurological conditions. Some causes may lead to gradual vision deterioration, while others can result in sudden and severe impairment. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for timely intervention and management.
Peripheral Vision Loss Causes
Glaucoma
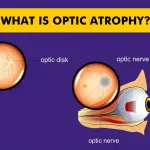
Glaucoma is a progressive eye disease that damages the optic nerve due to increased intraocular pressure. It is one of the most common causes of Peripheral vision loss, often developing slowly over time without noticeable symptoms. The condition affects the eye’s drainage system, leading to fluid buildup and increased pressure that damages the optic nerve.
The most common type, open-angle glaucoma, progresses silently and can go undiagnosed until significant peripheral vision is lost. Angle-closure glaucoma, a less common but more severe form, can cause sudden vision loss and severe eye pain. Early detection and treatment are crucial to slowing its progression and preventing permanent blindness.
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Retinitis pigmentosa is a genetic disorder that leads to the gradual degeneration of the retina’s photoreceptor cells. It initially affects night vision and later progresses to peripheral vision loss, resulting in tunnel vision symptoms. Over time, individuals may lose most of their peripheral sight, making it challenging to navigate spaces without assistance.
There is no definitive cure for retinitis pigmentosa, but various low-vision aids and therapies can help patients adapt to their vision changes. Research is ongoing to explore potential treatments, including gene therapy and retinal implants.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted due to a clot or bleeding, potentially affecting the visual processing areas. If the stroke impacts the occipital lobe or optic pathways, it can cause hemianopia, where half of the visual field is lost. Some individuals may experience peripheral vision loss in one or both eyes, making daily activities such as reading, driving, and recognising faces challenging.
Rehabilitation therapy and visual training may help stroke survivors adapt to their vision impairment and improve their ability to perform daily tasks.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. In its early stages, the condition may cause mild vision disturbances, but as it progresses, abnormal blood vessels develop and leak fluid, leading to swelling and retinal damage. This can result in peripheral vision loss and, in severe cases, total blindness.
Managing diabetes through diet, exercise, and medication can reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Treatments such as laser therapy and anti-VEGF injections may help slow disease progression.
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is an optic nerve inflammation commonly associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). It can cause sudden vision loss, blurred vision, and pain, particularly during eye movement. Peripheral vision loss due to optic neuritis may be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of nerve damage.
Treatment often involves corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and improve vision recovery. Managing underlying conditions such as MS is crucial to preventing recurrent episodes.
Retinal Detachment
A detached retina occurs when the retina pulls away from its supportive tissues, cutting off its oxygen and nutrient supply. This condition is a medical emergency that can cause sudden flashes of light, floaters, and a shadow over the peripheral vision. If not treated promptly, retinal detachment can lead to permanent vision loss.
Treatment options include laser surgery, pneumatic retinopexy, and scleral buckle procedures, which help reattach the retina and restore vision.
Brain Injuries and Tumours
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and tumours affecting the occipital lobe or optic pathways can disrupt visual processing, impairing peripheral vision. Depending on the severity and location of the injury, individuals may experience partial or total peripheral vision loss.
Rehabilitation therapy, surgery, or medications may help manage vision deficits caused by brain injuries and tumours.
What are the Symptoms of Peripheral Vision Loss?
- Colliding with things or people
- Difficulty driving or using steps, especially at night
- Night vision issues
- Trouble navigating busy or dimly lit areas
- A feeling of looking through a tunnel
- Need to turn your head to see surroundings
- Missing moving objects
Diagnosis
Peripheral Vision Test
Several tests are used to assess peripheral vision loss:
- Confrontation Visual Field Test: A simple test where the patient covers one eye while the examiner moves an object from the side to determine the field of view.
- Automated Perimetry: A computerised test that measures light detection across different visual field areas.
- Goldmann Visual Field Test: A manual test that maps peripheral vision using varying light intensity and movement.
Peripheral Vision Loss Treatment
Medications – Prescription eye drops or oral medications can be used to manage conditions such as glaucoma, which lowers intraocular pressure and prevents further vision loss.
Surgery – Surgical procedures like trabeculectomy, laser therapy, or vitrectomy may be necessary for conditions like glaucoma, retinal detachment, and diabetic retinopathy.
Vision Rehabilitation – Vision rehabilitation programs help patients with severe peripheral vision loss adapt to daily life using assistive devices and mobility training.
Living with Vision Loss
Assistive Devices – Wide-angle mirrors, mobility canes, and electronic visual aids can help individuals navigate their surroundings more safely.
Emotional Support – Counselling and support groups can help individuals cope with the challenges of peripheral vision loss.
Diagnosis
Peripheral Vision Test
Several tests are used to assess peripheral vision loss:
- Confrontation Visual Field Test: A simple test where the patient covers one eye while the examiner moves an object from the side to determine the field of view.
- Automated Perimetry: A computerised test that measures light detection across different visual field areas.
- Goldmann Visual Field Test: A manual test that maps peripheral vision using varying light intensity and movement.
How is it Prevented Peripheral Vision Loss?
While not all cases can be prevented, proactive care reduces the risk of permanent damage.
- Schedule regular eye exams, especially if you’re over 40 or have a family history
- Control blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels
- Wear protective eyewear
- Quit smoking
- Consume a nutrient-rich diet (e.g leafy vegetables, fish, and omega-3 fatty acids)
- Make your home easier to navigate
- Monitor for any sudden vision changes
Take proactive steps in managing your eye health. Schedule a comprehensive eye exam and explore available treatment options. Book Your Eye Consultation Today
FAQs
Peripheral vision refers to your ability to see objects and movement outside the direct line of sight, extending to the edges of your field of view.
Peripheral vision is crucial for tasks like driving, walking, and sports, as it provides awareness of the environment and helps maintain balance and coordination.
Peripheral vision problems can be caused by eye diseases like glaucoma, retinal detachment, optic nerve damage, neurological conditions, aging, or physical trauma.
Depending on the cause, some peripheral vision problems can be corrected or managed through treatments, rehabilitation, or adaptive techniques.
The two primary types of vision are central vision, which is focused and detailed, and peripheral vision, which provides a broader view but lacks detail.
Read here about types of low vision.
Peripheral vision may sometimes seem better due to its sensitivity to motion and changes in the environment, which are essential for rapid detection of potential hazards.
Peripheral vision is most crucial in situations that require awareness of surroundings, such as driving, sports, and navigating crowded spaces, where detecting movement or objects at the edges of your field of view is critical.
Early signs include difficulty seeing in dim lighting, frequent tripping over objects, and tunnel vision symptoms. Some individuals may also notice increased sensitivity to bright light or trouble detecting motion from the sides.
The possibility of reversal depends on the cause. Some conditions, like retinal detachment, can be treated successfully if addressed early, while others, like glaucoma, can only be managed to slow progression rather than fully restore vision.
An ophthalmologist can conduct a peripheral vision test, such as automated perimetry or Goldmann visual field testing, to assess the extent of vision impairment and determine the underlying cause.