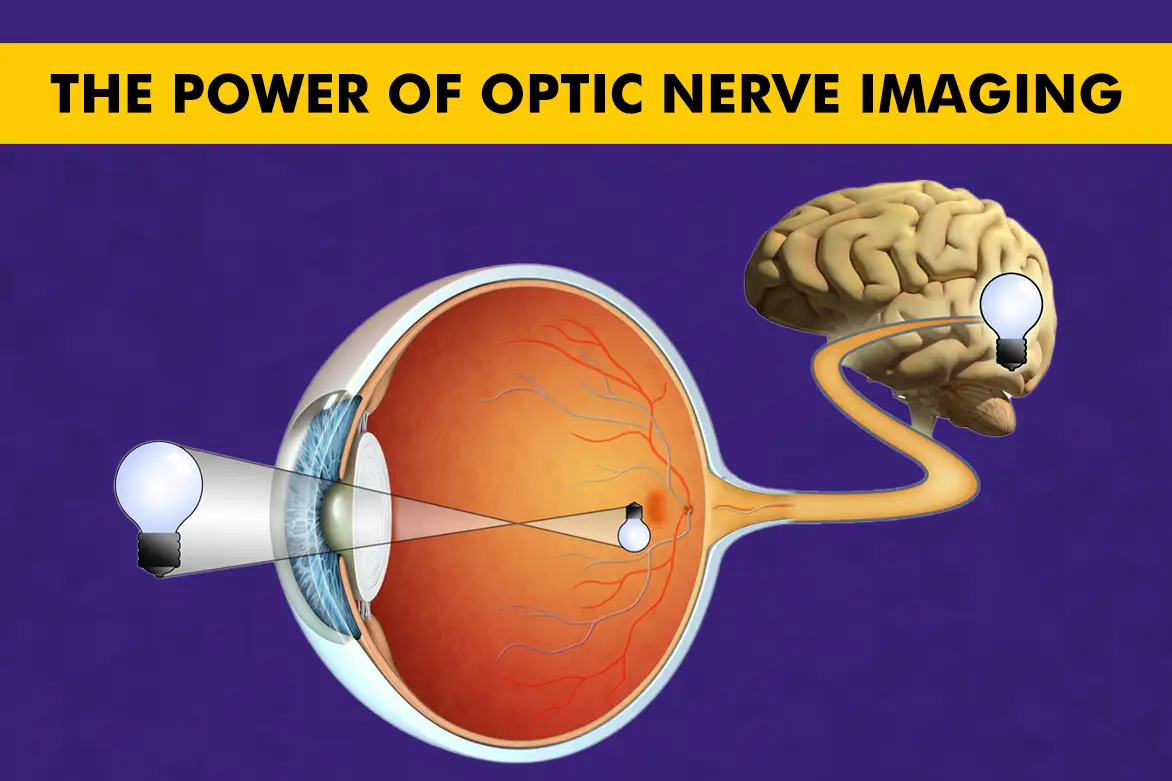
Optic nerve imaging plays a significant role in preserving eye health, allowing for the early detection of conditions that can lead to vision loss. This non-invasive procedure helps eye care professionals assess the health of the optic nerve, which is vital in transmitting visual information from the eyes to the brain. Early detection of optic nerve issues, such as those caused by glaucoma or other diseases, is essential in preventing irreversible vision impairment. Regular scans allow patients to safeguard their vision and receive timely treatment to maintain optimal eye function.
Understanding the Function of Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is a fundamental part of the visual system, responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. This nerve consists of over one million nerve fibres, working collectively to deliver clear, undistorted images, enabling the optimum function of the optic nerve. Maintaining a healthy optic nerve is essential for proper vision. Routine monitoring through imaging can help detect changes early, preserving vision and supporting overall eye health.
Primary Purpose of Optic Nerve Imaging
- Diagnosis and Monitoring of Eye Conditions: It is primarily used to diagnose and monitor various eye conditions. Diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, and optic nerve tumours can be detected early through advanced imaging techniques. This early diagnosis is key in preventing further complications and guiding treatment strategies for better outcomes. For patients at higher risk, regular imaging helps eye care professionals monitor the optic nerve’s health and detect any changes over time.
- Assessing Optic Nerve Damage: Imaging also plays a crucial role in assessing the extent of optic nerve damage, especially in cases of trauma or existing conditions like glaucomatous optic nerve atrophy. This way, doctors can better recommend appropriate interventions.
Optic Nerve Imaging Techniques Available in India
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT is a non-invasive imaging technique that captures detailed cross-sectional images of the optic nerve and retina. It is particularly useful for detecting early changes in the nerve fibre, helping diagnose conditions like glaucoma before significant damage occurs. Observing subtle changes, OCT provides a clear picture of the optic nerve.
Fundus Photography
Fundus photography captures high-resolution images of the retina and optic disc, offering a comprehensive view of the optic nerve head. These images help eye care professionals assess the structure of the optic nerve and monitor any abnormalities that may indicate the onset of disease or injury.
MRI and CT Scans
MRI of the optic nerve or CT scans may be employed for more complex cases, such as suspected tumours or severe nerve compression. These imaging techniques allow for a detailed view of the entire optic nerve and surrounding structures, enabling the detection of abnormalities that may not be visible through other methods. It is particularly effective in detecting tumours or inflammation.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound is another non-invasive method for examining the optic nerve. This technique is beneficial for detecting swelling or inflammation in the optic nerve, often seen in conditions like optic neuritis. Ultrasound provides a quick, accessible way to assess the nerve without radiation or extensive equipment.
Purpose of Optic Nerve Imaging for Specific Conditions
Glaucoma
One of the primary uses of optic nerve imaging is to monitor changes associated with glaucoma and optic nerve damage. In this condition, the optic nerve gradually deteriorates due to increased pressure inside the eye, leading to progressive vision loss. Regular imaging helps detect early signs of glaucomatous optic nerve atrophy, enabling timely intervention to manage the condition and prevent further damage.
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the optic nerve, often associated with autoimmune disorders like multiple sclerosis. Imaging helps detect inflammation and assess the degree of damage, allowing doctors to devise an appropriate treatment plan that can help preserve or restore vision.
Optic Neuropathy
Optic neuropathy involves the loss of nerve fibres within the optic nerve, leading to vision problems. Optic nerve imaging is essential in identifying the cause and extent of nerve fibre loss and guiding treatment.
Looking for a trusted eye care specialist in India? Book an appointment with specialists from Centre for Sight
Ensuring Optic Nerve Health
Taking proactive care of your optic nerve can support long-term visual health. Here are some tips to help prevent damage:
- Manage chronic conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes effectively, as they can affect the optic nerve.
- Maintain a balanced lifestyle with regular exercise and a diet rich in eye-friendly nutrients, like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants.
- Avoid smoking and limit exposure to harmful factors, such as UV rays.
- Undergo routine eye exams, especially if you are at risk for optic nerve-related diseases.
Consistent screenings can help ensure timely treatment, preserving your vision and overall eye health. If you’re at risk, scheduling regular screenings is a valuable step to safeguard your vision.
FAQs
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is widely regarded as the best imaging modality for evaluating the optic nerve. It offers high-resolution images that help detect structural changes associated with conditions like glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
The retina captures light and converts it into electrical signals through photoreceptors. These signals are transmitted to the optic nerve via retinal ganglion cells, which relay visual information to the brain.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging technique for diagnosing optic neuritis. It effectively visualises the optic nerve and can identify inflammation or lesions indicative of the condition.