|
Key Takeaways:
|
Optic atrophy is a condition where damage to the optic nerve reduces how clearly you see. It’s tricky because the changes can be slow and subtle at first, making optic atrophy symptoms easy to miss.
In this guide, you’ll learn the causes, signs, tests, and real-world options for optic atrophy treatment in India so you can act early and protect your vision.
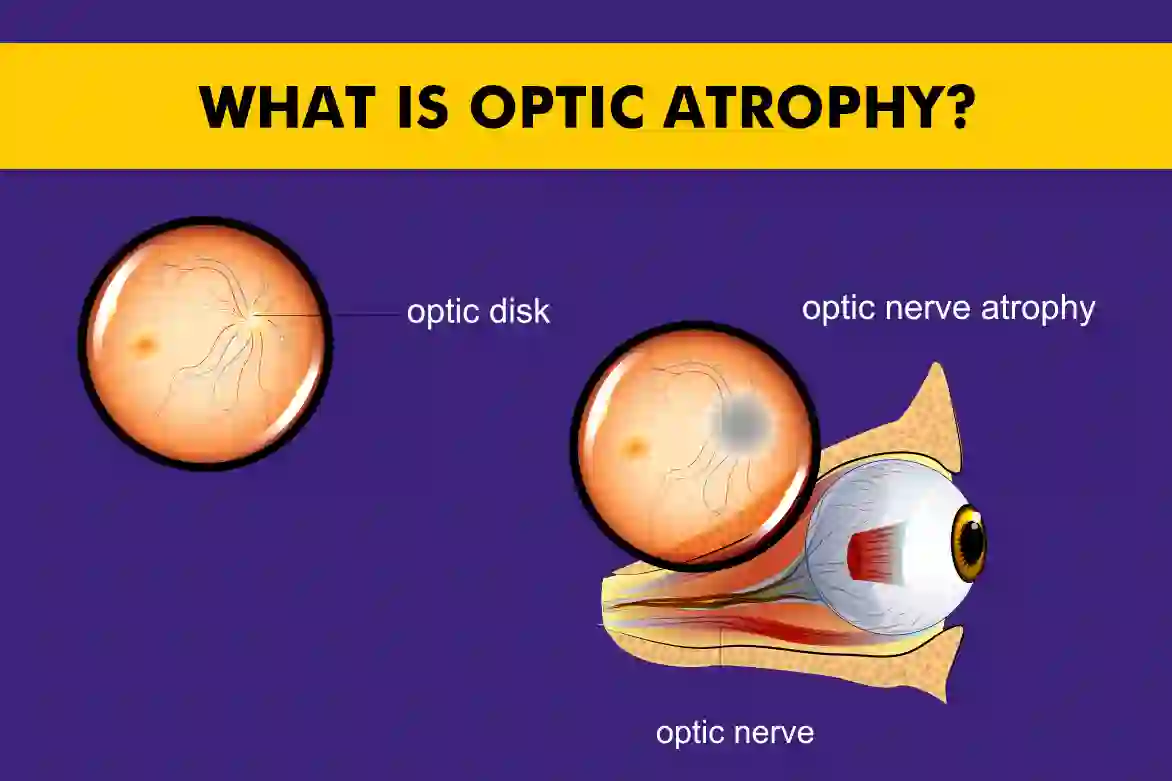
What Is Optic Atrophy?
Optic atrophy results from damage or degeneration of the optic nerve, the nerve by which visual information is conducted to your eyes and your brain. When the nerve is damaged, your vision is compromised, sometimes permanently.
While there is no definitive optic atrophy cure, timely detection and management can help preserve remaining vision.
Optic Atrophy Causes
Numerous conditions and risk factors can cause optic atrophy. Below are the most common optic atrophy causes:
- Decreased Blood Flow (Ischemic Optic Neuropathy):
Most commonly seen in older adults, decreased blood supply to the optic nerve is a leading cause of optic atrophy.
- Eye Disorders:
Glaucoma, optic neuritis, and papilledema are potential causes for damage to the optic nerve.
- Neurological Disorders:
Brain tumour, multiple sclerosis, stroke, or cranial arteritis can influence optic nerve health.
- Hereditary Disorders:
Genetic disorders like Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy can cause optic atrophy even in young patients.
- Trauma or Injury:
Contusion, resulting from an accident or foreign bodies, causes injury to the nerve.
- Infections:
Infections like syphilis, tuberculosis, Lyme disease, measles, and fungal infections like aspergillosis can infect the optic nerve.
- Vitamin Deficiencies:
Vitamin B deficiencies (particularly B1, B2, B6, B9, and B12) have been associated with issues of the optic nerve.
- Chronic Stress and Anxiety:
Chronic stress may indirectly lead to nerve damage over time.
Optic Atrophy Types
Below are the 2 (two) principal optic atrophy types :
- Primary Optic Atrophy: Damage to the nerve without preceding swelling.
- Secondary Optic Atrophy: Damage to the nerve caused by swelling or inflammation.
What are the Optic Atrophy Symptoms?
Early warning signs are subtle but cannot be dismissed. Below are the common optic atrophy symptoms:
- Slow or fuzzy vision loss
- Blurry vision
- Reduced sharpness or contrast sensitivity
- Reduced colour perception
- Reduced field of vision (particularly peripheral vision)
If any of these occur, get an eye specialist as quickly as possible. Identifying optic atrophy symptoms early improves the chances of preserving vision through timely intervention.
Optic Atrophy Diagnosis
Physicians employ a mix of eye and imaging examinations to screen whether atrophy of the optic nerve is occurring and what its cause would be.
Equipment employed for typical tests is:
- Ophthalmic Exam: An in-depth study of your optic nerve and retina.
- Visual Field Testing: To screen for blind spots or vision loss in peripheral vision.
- MRI or CT Scans: To exclude brain abnormalities or nerve damage.
- Blood Tests: To identify infection or deficiency.
Early diagnosis offers a better opportunity to slow its progression and save your existing vision through appropriate optic nerve atrophy treatment.
Optic Atrophy Treatment
Unfortunately, the optic nerve cannot be restored once injured. That is, there is no optic atrophy, yet all hope is not lost. The goal of optic atrophy treatment is to halt further injury and address the cause.
For instance:
- Optic atrophy due to glaucoma can be treated by employing eye drops or surgery to lower eye pressure.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases are sometimes treated with corticosteroids or other drugs.
- Nutrition deficiencies can sometimes be replaced with supplements and dietary adjustments.
While lost vision is usually not recoverable, early and constant care, through proper optic nerve atrophy treatment, can save current vision and enhance quality of life.
Conclusion
Optic atrophy means the optic nerve is damaged, so protecting the vision you have left is the goal. Early warning signs can be small, but timely tests and treatment plans, plus low-vision rehab where needed, make a real difference. Since causes vary, management should be tailored to you, rather than copied from someone else. If you notice new vision changes, book an eye specialist or a neuro-ophthalmologist to get a proper diagnosis and next steps.
FAQs
What causes optic atrophy?
Optic atrophy is caused by damage to the optic nerve, which can result from conditions like glaucoma, stroke, inflammation, or trauma. It can also be hereditary in some cases.
What is the life expectancy of someone with optic atrophy?
Optic atrophy does not directly affect life expectancy. However, managing the underlying causes is important to maintain overall health and quality of life.
Do glasses help optic nerve atrophy?
While glasses can improve specific vision issues, they do not treat or improve vision loss caused by optic atrophy. Treating the underlying cause is essential to managing the condition
Is optic atrophy always permanent?
Vision loss is generally irreversible, although early intervention can stop vision loss and preserve existing vision. While there may not be a full optic atrophy cure, managing it is possible.
Who is most at risk for Optic Atrophy?
The most at risk for Optic Atrophy are older adults, persons with chronic illness (e.g., diabetes or hypertension), persons with a family history of nerve disease, and persons with active infection or trauma.