Summary: Myopia and hypermetropia affect vision differently, but both stem from irregular eye shape. Understanding their symptoms and correction options helps individuals choose effective treatments and maintain long-term eye health.
|
Key Takeaways:
|
Refractive errors are common eye conditions that affect how light is focused on the retina, leading to blurred vision. Among these, myopia (nearsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness) are the most frequently diagnosed. While both involve problems with how the eye bends light, their causes, symptoms, and treatments are quite different. Recognizing the difference between myopia and hypermetropia is crucial for early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and effective management.
This article focuses on the myopia vs hypermetropia, offering a detailed comparison while briefly covering their symptoms, causes, and correction options.
Understanding What is Myopia and Hypermetropia
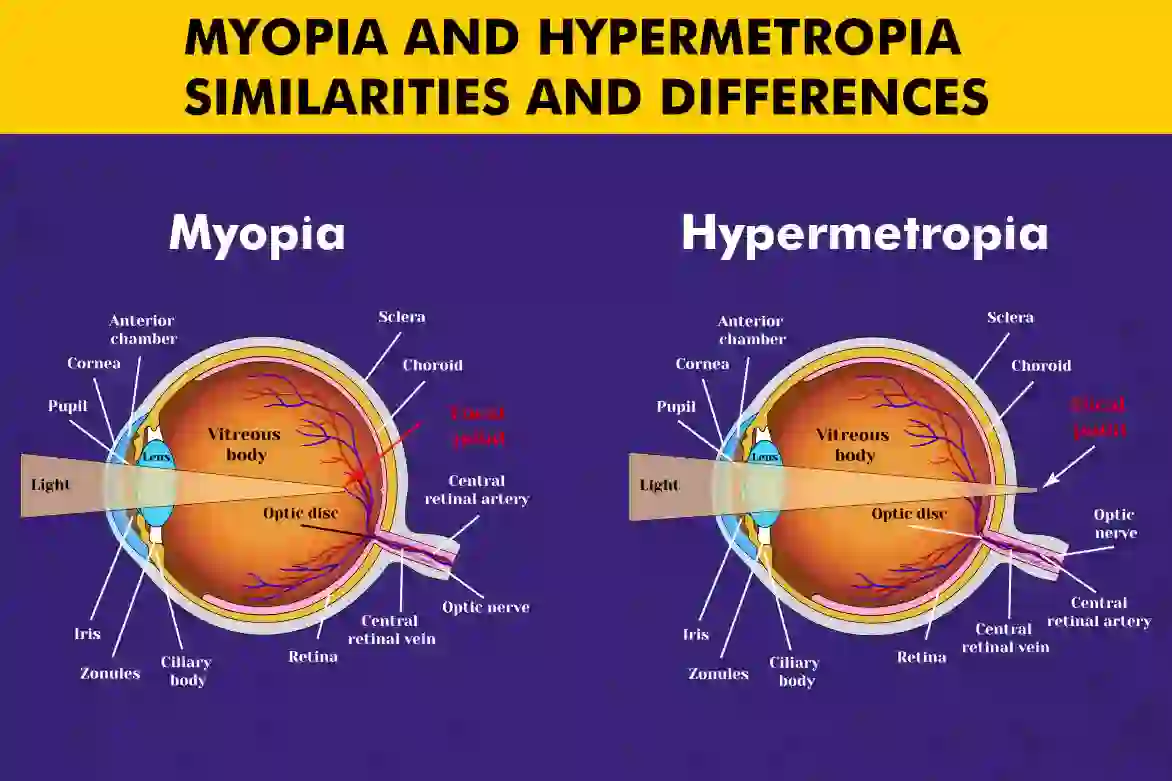
Myopia (nearsightedness) is a refractive error where distant objects appear blurry while close objects remain clear. The eyeball is usually longer than normal, causing light to focus in front of the retina.
Hypermetropia (farsightedness) makes nearby objects difficult to see clearly, while distance vision is clearer; in this case, the eyeball is shorter than average, so light focuses behind the retina.
Key Reasons Behind Myopia and Hypermetropia
Myopia typically develops due to an elongated eyeball or an overly curved cornea. Genetics strongly influence its development, and excessive screen time, prolonged reading, or close-up work can worsen the condition.
Hypermetropia, on the other hand, is caused by a smaller-than-normal eyeball or a flatter cornea, which pushes the focal point behind the retina. Hereditary factors and age-related changes also contribute to one of the key causes of hypermetropia.
Symptoms – How Myopia and Hypermetropia Affect Vision
Symptoms of Myopia
People with myopia experience:
- Blurred vision when viewing distant objects, such as road signs or chalkboards.
- Frequent squinting to improve clarity.
- Eye fatigue and headaches after focusing on distant tasks for extended periods.
Symptoms of Hypermetropia
Individuals with hypermetropia report:
- Blurred vision while reading or using digital devices.
- Eye strain, especially during prolonged near work.
- Headaches, particularly around the forehead.
While both conditions can cause visual discomfort, the symptoms differ based on the range of vision affected.
Key Differences Between Myopia and Hypermetropia
To better understand the difference between myopia and hypermetropia, let’s compare their key characteristics:
| Aspect | Myopia (Nearsightedness) | Hypermetropia (Farsightedness) |
| Vision | Clear near vision; blurry distance vision | Clear distance vision; blurry near vision |
| Focal Point of Light | In front of the retina | Behind the retina |
| Eyeball Shape | Elongated eyeball | Shortened eyeball |
| Corneal Shape | Steep curvature | Flatter curvature |
| Symptoms | Difficulty seeing far, eye strain, headaches | Difficulty reading or focusing on near objects, eye strain, headaches |
| Corrective Lens Type | Concave lenses (minus lenses) | Convex lenses (plus lenses) |
| Common Age of Onset | Childhood or adolescence | Present at birth or worsens with age |
| Progression | Can worsen rapidly during childhood | Often stable but may worsen with age |
Myopia vs Hypermetropia – Correction and Treatment Options
Despite their differences, both conditions can be effectively managed with corrective measures.
Myopia Correction Options
- Concave Lenses: These lenses shift the focal point backward onto the retina, improving distance vision.
- Refractive Surgery: Procedures like LASIK and SMILE reshape the cornea to address the refractive error.
- Orthokeratology: Special contact lenses worn overnight temporarily reshape the cornea, reducing dependency on glasses.
Hypermetropia Correction Options
- Convex Lenses: Plus lenses help converge light rays, focusing them directly on the retina.
- Refractive Surgery: LASIK and PRK can permanently reshape the cornea to correct hypermetropia.
- Eye Exercises: Focusing exercises may help reduce strain, although they cannot “cure” hypermetropia.
Myopia and Hypermetropia Lens Types
- Myopia Lenses: Concave lenses have a thinner center and thicker edges to diverge light rays.
- Hypermetropia Lenses: Convex lenses are thicker at the center, converging light rays for proper focus.
Preventing Refractive Errors
Refractive errors like myopia and hypermetropia can be managed or slowed with proper habits and proactive measures.
Tips for Myopia Prevention
- Encourage Outdoor Activities: Spending time outdoors reduces the risk of myopia in children by promoting healthy eye development.
- Limit Screen Time: Follow the 20-20-20 Rule take a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away.
- Maintain Proper Lighting and Posture: Ensure a well-lit workspace and avoid slouching during reading or near work.
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in Vitamin A, C, and Omega-3s, such as leafy greens, carrots, and fish, to support eye health
Managing Hypermetropia
- Use Corrective Lenses: Wear prescribed convex lenses to improve near vision and reduce eye strain.
- Eye Exercises: Perform simple exercises like pencil push-ups or focus shifting to improve focusing ability.
- Routine Eye Exams: Regular check-ups are essential to update prescriptions and monitor age-related changes.
- Optimize Workspaces: Adjust reading materials and screens for comfortable viewing, and use proper lighting.
General Tips for Healthy Vision
- Protect eyes from UV rays with sunglasses.
- Stay hydrated to prevent eye dryness.
- Avoid rubbing eyes to reduce the risk of infections or corneal damage.
Conclusion
The difference between myopia and hypermetropia lies in how they affect vision, the structure of the eye, and their respective correction methods. While myopia impairs distance vision, hypermetropia affects near vision. Both conditions can be effectively managed with proper diagnosis, corrective lenses, or advanced surgical options.
Regular eye checkup and adopting healthy habits, such as limiting screen time and spending time outdoors, can help manage and prevent these refractive errors. If you experience blurred vision or other symptoms, consult an eye specialists for timely advice and treatment.
FAQs
Is myopia plus or minus?
Myopia is commonly referred to as nearsightedness and is denoted as a negative value in terms of diopters. So, myopia is indicated by a minus (-) sign.
Is hypermetropia lens plus or minus?
Hypermetropia is commonly referred to as farsightedness and is denoted as a positive value in terms of diopters. So, hypermetropia is indicated by a plus (+) sign.
Is hyperopia better than myopia?
Neither hyperopia nor myopia is inherently better than the other. The impact of these conditions on vision varies depending on the individual and the degree of refractive error. Both conditions can be effectively managed with appropriate corrective measures.
Can you be nearsighted in one eye and farsighted in the other?
Yes, it is possible to have different refractive errors in each eye. This condition is known as anisometropia. An individual may be nearsighted (myopic) in one eye and farsighted (hypermetropic) in the other.
What is the difference between myopia and hypermetropia?
The main difference between myopia and hypermetropia lies in how light is focused by the eye. In myopia, light focuses in front of the retina, causing blurry distance vision. In hypermetropia, light focuses behind the retina, resulting in blurry near vision.
What is myopia and hyperopia?
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a refractive error that affects the ability to see distant objects clearly. Hypermetropia, also known as farsightedness, is a refractive error that affects the ability to see nearby objects clearly.
Is myopia plus or minus?
Myopia is commonly referred to as nearsightedness and is denoted as a negative value in terms of diopters. So, myopia is indicated by a minus (-) sign.
Is hypermetropia lens plus or minus?
Hypermetropia is commonly referred to as farsightedness and is denoted as a positive value in terms of diopters. So, hypermetropia is indicated by a plus (+) sign.
Is hyperopia better than myopia?
Neither hyperopia nor myopia is inherently better than the other. The impact of these conditions on vision varies depending on the individual and the degree of refractive error. Both conditions can be effectively managed with appropriate corrective measures.
Can you be nearsighted in one eye and farsighted in the other?
Yes, it is possible to have different refractive errors in each eye. This condition is known as anisometropia. An individual may be nearsighted (myopic) in one eye and farsighted (hypermetropic) in the other.
Can children outgrow hypermetropia?
Yes, mild hypermetropia in children may improve as the eyeball grows and develops. However, regular eye check-ups are essential.
What is hypermetropia and how can it be corrected?
Hypermetropia, or farsightedness, is a refractive error where distant objects are clear, but nearby objects appear blurry. It can be corrected with convex lenses (glasses or contact lenses) or refractive surgeries like LASIK to focus light properly on the retina.