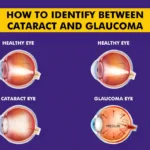
Glaucoma: One of the Leading Cause of Blindness Worldwide Glaucoma is an umbrella term for a group of diseases that cause irreversible loss of vision by damaging the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting information from our eyes to our brain. One of the leading causes of blindness worldwide, glaucoma increases intraocular pressure of the eye by tampering with the eye’s natural mechanism that drains aqueous humor, a fluid present in our eyes. This increased intraocular pressure due to the build-up of the fluid damages the optic nerve, which results in loss of vision.
Types of Glaucoma
We can classify glaucoma into different types like Open-Angle Glaucoma, Normal Tension Glaucoma, Narrow-Angle Glaucoma, and Secondary Glaucoma. For this blog, we’ll only focus on Open-Angle Glaucoma and Narrow-Angle Glaucoma in this section.
Open-Angle Glaucoma (Chronic):
- Open-angle glaucoma, also called chronic glaucoma, is the most commonly found form of the disease. This type of glaucoma doesn’t show any symptoms until a significant amount of vision is lost, which is why it is also known as “the silent thief of sight”.
- In this type of glaucoma, the drainage canal of our eye is not anatomically blocked but just clogged and the build-up of aqueous humor increases intraocular pressure which damages the optic nerve by causing the death of retinal ganglion cells (RGC).
- Chronic glaucoma runs in the family and anyone over the age of 40 with a family history of the disease should get regular eye checkups done to ensure they stay safe from the disease.
Narrow-Angle Glaucoma (Acute):
- Narrow-angle glaucoma is also known as acute glaucoma. It is not commonly found except in some parts of Asia. This is due to the anatomical structure of the eyes found in the population of those areas which is more vulnerable to this type of glaucoma.
- Patients suffering from acute glaucoma naturally have very narrow drainage canals in their eyes, which can suddenly close off and dramatically increase intraocular pressure of the eye. Whereas chronic glaucoma takes away vision slowly, this type can cause rapid irreversible loss of vision.
- Acute glaucoma is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. The symptoms of acute glaucoma include a red painful eye, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and a headache.
Acute Glaucoma: An Inflammatory Disease?
Acute glaucoma is characterized by a sudden and dramatic rise in intraocular pressure and as a consequence, the death of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) which leads to loss of vision. Even though acute glaucoma can be treated by medical and surgical methods, sometimes permanent damage to vision still occurs.
Researchers in the United States and China have made some observations in a study to understand the underlying mechanism that causes RGC death due to acute glaucoma. The researchers studied glaucoma in mice and came to two conclusions:
- Acute glaucoma in mice shows up as an inflammatory disease.
- Increased intraocular pressure causes vision loss by an inflammatory response, similar to one caused by bacterial infections which leads to programmed cell death (apoptosis) of retinal cells in mice.
To confirm that vision lost to glaucoma is due to an inflammatory response in mice, theresearchers proved that retinal cell death could be slowed in mice by suppressing either the TLR4 gene or caspase-8 protein. Caspase-8 protein inhibitors are already being used in clinical trials for treating cancer and stroke.
Implications
Even though research is still ongoing and these findings have only been proven true for mice, the implications of acute glaucoma being an inflammatory disease can help in finding more efficient screening and treatment for the disease in the future. Also Read: मोतियाबिंद इन हिंदी