High blood pressure (hypertension) is a common condition that impacts the heart and blood vessels. However, many are unaware that it can also seriously affect vision. One of the eye conditions linked to elevated blood pressure is hypertensive retinopathy.
In this guide, we get into what is hypertensive retinopathy, and explore its causes, risk factors, and treatment options available in India to help you safeguard your vision.
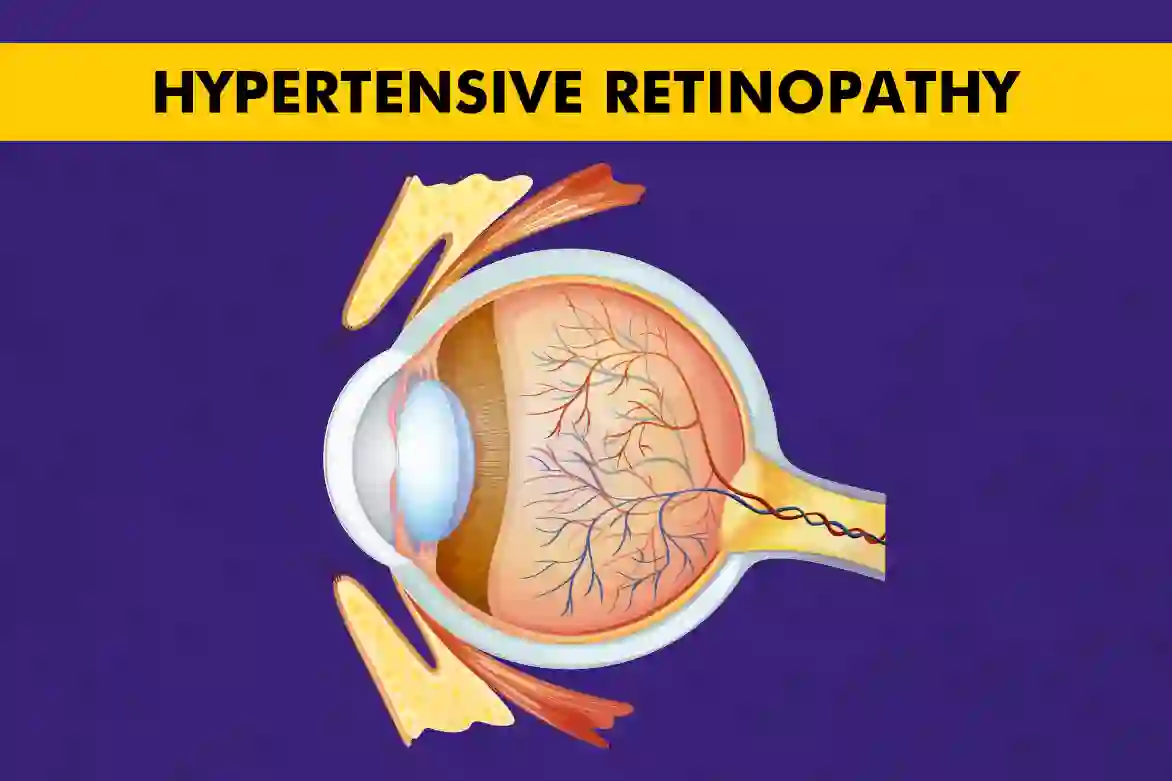
What is Hypertensive Retinopathy?
This condition happens when high blood pressure affects the blood vessels in the retina (the part of the eye that catches light and sends visual signals to the brain). Over time, this damage can cause vision issues, especially if hypertension remains uncontrolled. It is progressive in nature, ranging from mild changes to severe retinal damage that can result in significant vision loss.
Often, this condition develops without noticeable symptoms, making regular eye exams crucial for early detection. An ophthalmologist can identify subtle signs such as narrowed retinal arteries, swelling, or haemorrhages in the retina. Detecting these changes early is essential for hypertensive retinopathy management and can significantly reduce the risk of permanent vision loss.
Stages of Hypertensive Retinopathy
Understanding the stages of hypertensive retinopathy is critical to recognising its progression and initiating timely treatment.
- Mild Stage: The earliest stage is characterised by narrowing retinal arteries due to high blood pressure. Typically, there are no visible symptoms of hypertensive retinopathy at this stage, making it difficult to detect without an eye exam.
- Moderate Stage: As blood pressure rises, small haemorrhages (tiny areas of bleeding) and fatty deposits, known as exudates, may form in the retina. These changes can cause vision to blur or appear distorted.
- Severe Stage: In the most advanced stage, swelling of the optic nerve (known as papilledema) and extensive retinal damage can occur. This stage is more likely to occur in patients with uncontrolled, long-standing hypertension.
Recognising these stages early allows for prompt treatment for hypertensive retinopathy, which is crucial in preventing further retinal damage and maintaining visual health.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of hypertensive retinopathy is persistently high blood pressure, which exerts excessive force on the delicate blood vessels in the retina. This prolonged pressure causes the vessels to narrow, harden, or bleed. However, with the proper treatment, it can be managed.
Other contributing risk factors include:
- Long-term, uncontrolled hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure puts continuous stress on the retina, accelerating damage.
- Cardiovascular conditions: Coexisting conditions like heart disease or high cholesterol increase the likelihood of retinal damage.
- Age and genetic predisposition: Older adults and individuals with a family history of hypertension are at a greater risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Habits such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise can increase blood pressure and elevate the risk of developing hypertensive retinopathy.
Want to protect your vision from hypertensive retinopathy?
Consult an Eye Specialist Today!
Symptoms of Hypertensive Retinopathy
In the initial stages, there may not be any noticeable signs of hypertensive retinopathy, making regular eye examinations crucial for early detection. As the condition progresses, symptoms may manifest, indicating damage to the retinal blood vessels. These symptoms include:
- Blurred or Double Vision: Damage to the retina can disrupt normal visual processing, leading to blurriness or a doubling of images.
- Reduced Visual Clarity: Vision may gradually become less sharp, making it difficult to see fine details.
- Sudden Vision Loss: In advanced cases, a sudden and significant change in vision can occur, signalling severe retinal damage.
- Headaches and Eye Strain: Increased pressure within the eyes can cause discomfort, leading to headaches or eyestrain.
Because this condition can silently progress without obvious signs, routine eye exams are essential for the early identification and management of hypertensive retinopathy.
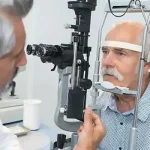
Diagnosis of Hypertensive Retinopathy
To diagnose hypertensive retinopathy, an eye specialist will conduct a fundoscopy. This procedure involves using an ophthalmoscope to examine the back of the eye, specifically looking at the blood vessels in the retina for signs of narrowing, swelling, or bleeding. Based on these findings, the doctor can determine the grade of hypertensive retinopathy.
In certain cases, additional tests may be recommended:
- Fluorescein Angiography: A special dye is added into the bloodstream to highlight the blood vessels in the retina, allowing the doctor to visualise any blockages or abnormal blood flow.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This advanced imaging test produces detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, providing precise information on the extent of retinal damage.
Since high blood pressure is the primary cause of hypertensive retinopathy, ongoing blood pressure monitoring is an integral part of both diagnosing and managing the condition.
Now that we have covered the stages, causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of hypertensive retinopathy, let’s explore the management strategies.
Treatment and Management
The cornerstone of treating hypertensive retinopathy is effectively managing your blood pressure. Since high blood pressure is the main cause of this condition, controlling it is crucial for preventing more damage to the retinal blood vessels and maintaining overall eye health. Treatment strategies may include:
- Medications: Blood pressure medications are often prescribed to lower blood pressure. Depending on your specific health requirements, these may include beta-blockers, diuretics, or ACE inhibitors.
- Lifestyle Changes: Following a healthier lifestyle is essential. Eating a balanced diet low in sodium, doing regular exercise, and not smoking are all effective ways to keep blood pressure under control and lower the risk of further retinal damage.
- Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye check-ups such as retina scans are critical for monitoring the condition of the retina and detecting any new changes.
Living with Hypertensive Retinopathy
Living with this condition requires consistent management of your overall health. Regular follow-ups with your eye doctor and general physician are essential to keep blood pressure levels stable and monitor any eye changes. By catching hypertensive retinopathy signs and symptoms early on to controlling blood pressure, most individuals can prevent the condition from worsening and maintain good vision.
For expert care, visit Centre for Sight to discuss your options and incorporate routine eye exams into your comprehensive health care plan.
Stay ahead of vision problems!
FAQs
Diabetic retinopathy often involves abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina. It is caused by diabetes, while hypertensive retinopathy is characterised by narrowed or leaking vessels caused by high blood pressure. Both conditions affect the retina but have different underlying causes and patterns of damage.
Yes, high blood pressure can significantly affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to complications like retinal damage. Over time, if untreated, this can result in vision problems or even permanent vision loss.