|
Key Takeaways:
|
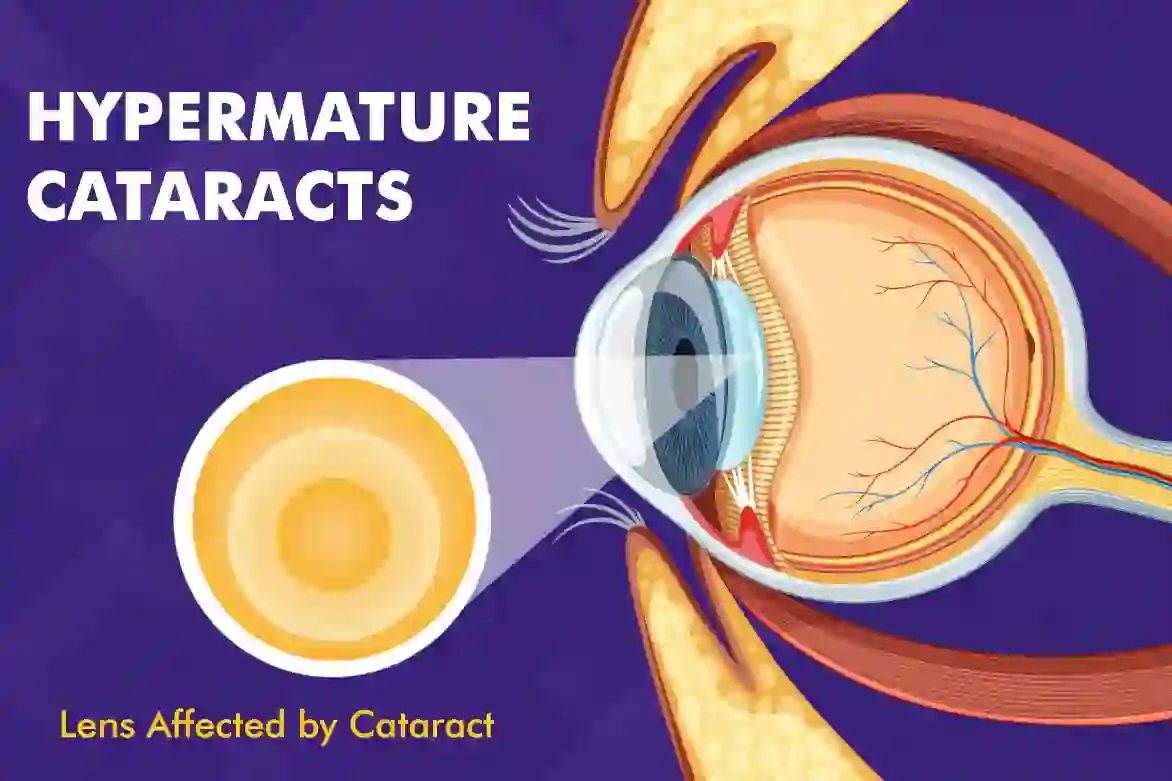
Hypermature cataract is a highly advanced form of cataract where the natural lens becomes extremely hard or starts to liquefy, resulting in cloudy and distorted vision. At this stage, cataract surgery is often the most effective treatment to restore vision.
People wait because the blur builds slowly, making it non-threatening at first. However, by this stage, glare, discomfort, and risks such as high eye pressure can increase.
In this blog, we explain what a hypermature cataract is, how it differs from earlier stages, the key symptoms and red flags, and the treatment options, including both surgical and non-surgical options.
What is a Hypermature Cataract?
A hypermature cataract is an advanced stage of cataract development. If left untreated, it becomes dense, rigid, and opaque like a pearl.
These cataracts are challenging to remove and can lead to complete vision loss. Hypermature cataracts may have fluid buildup inside them.
In severe cases where fluid accumulates excessively and the nucleus size decreases, it’s known as a Morgagnian cataract, which requires special treatment considerations. Additionally, untreated hypermature cataracts can lead to the development of other eye conditions and increase the risk of blindness.
Hypermature Cataract Symptoms
As cataracts progress to the hypermature stage, they become denser, causing significant vision impairment. Tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces become increasingly challenging.
Additionally, hypermature cataracts can lead to inflammation and increased pressure within the eye, potentially causing additional eye conditions and elevating the risk of blindness.
Symptoms of hypermature cataracts can vary in severity from person to person, with some experiencing more pronounced vision loss than others. It’s essential to address hypermature cataracts promptly to prevent further complications and preserve vision.
Untreated hypermature cataracts significantly increase the risk of vision loss and blindness. Therefore, early detection and timely treatment are crucial to maintaining eye health and quality of life.
Causes of Hypermature Cataract
Below are the causes of hypermature cataract:
- Age factor: A hypermature cataract is primarily associated with aging, becoming more prevalent after the age of 60.
- Genetic influence: Genetic predisposition can play a significant role in the development of hypermature cataracts. Individuals with a family history of cataracts are at a higher risk of developing them.
- UV radiation exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation without adequate eye protection can contribute to the formation of cataracts, including hypermature cataracts.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of developing hypermature cataracts. The impact of high blood sugar levels on lens health can accelerate the formation of cataracts.
- Eye trauma: Traumatic events, such as injuries to the eye, can accelerate the development of hypermature cataracts. Damage to the eye’s structures can promote cataract formation.
- Smoking: Smoking is a modifiable risk factor associated with an increased susceptibility to cataracts, including hypermature cataracts. Chemicals in tobacco smoke can accelerate the aging process of the lens.
- Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, particularly corticosteroids, may contribute to the development of hypermature cataracts. It’s essential to discuss the potential side effects of medications with a healthcare provider.
- Previous eye surgeries: Individuals who have undergone previous eye surgeries or procedures may have an increased risk of developing hypermature cataracts. Surgical interventions can alter the structure and function of the eye, potentially leading to the formation of cataracts.
Stages of Cataract
Below are the four different stages of cataract:
- Early Cataracts (Immature): Initial stage with minimal clouding of the eye’s lens.
Symptoms of early cataracts: Slight blurriness, mild visual discomfort. - Intermediate Cataracts (Mature): Description: Advancing opacity of the lens, causing noticeable vision impairment.
Symptoms of intermediate cataract: Increased blurriness, glare sensitivity. - Advanced Cataracts (Mature): Significant clouding, leading to substantial vision decline.
Symptoms of advanced cataracts: Severe blurriness, not allowing for useful vision. - Hypermature Cataracts: Final stage with a fully clouded lens, impacting overall vision.
Symptoms: Progressive vision loss, ultimately leading to blindness, with only the perception of light remaining.
Diagnosis of Hypermature Cataract
Below is the diagnostic procedure for hypermature cataract:
- Patient history and symptom analysis:
Eye doctors initiate the diagnostic journey by collecting a thorough patient history, discussing past eye-related issues and relevant medical conditions.
They also scrutinize symptoms reported by the patient, such as diminished visual acuity, heightened sensitivity to light, color perception changes, and any associated discomfort.
- Visual acuity examination:
A meticulous visual acuity assessment using standardized eye charts is necessary to gauge both near and distance vision.
This step lays the foundation for understanding the extent of vision impairment and guiding subsequent diagnostic decisions.
- Slit lamp evaluation:
A slit lamp is used for a detailed examination of the anterior eye segment, providing crucial insights into the opacity, density, and color of the hypermature cataract. This helps identify any corneal edema or additional complications that influence the treatment strategy.
- Pupil dilation:
This test is performed to provide a clearer view of the lens.
- Gonioscopy for glaucoma assessment:
In instances of suspected secondary glaucoma, gonioscopy helps assess the angle between the iris and cornea. This step is vital for uncovering potential angle-closure complications associated with hypermature cataracts.
- Biometry:
Biometry is important for measuring axial length and calculating the optimal intraocular lens (IOL) power, which is essential for planning cataract surgery.
- Ultrasonography (USG)
Ultrasonography (USG), helps obtain detailed images of the lens and its surrounding structures. Also, in hypermature cataracts, the retina may not be directly visualised. Ultrasonography provides key details about the retina.
- Endothelial cell count:
Gauge the health of the corneal endothelium by measuring endothelial cell density, particularly relevant for surgical considerations. A decreased cell count may signify potential challenges during cataract surgery, necessitating careful planning.
When to Treat (Red Flags for Surgery)
Treatment is planned as early as possible as a hypermature cataract significantly impairs vision and can lead to secondary complications like glaucoma.
Red flags that need prompt surgery:
- Sudden pain, redness, or a quick drop in vision (could mean pressure or inflammation is rising).
- Very hard or white-looking lens with poor view inside the eye (common in a hypermature cataract).
- High eye pressure or signs of lens-related inflammation (doctors call it lens-induced glaucoma/uveitis).
- One good eye only (the affected eye is your only seeing eye), or you’re at risk of falls/accidents because of vision.
- Poor view of the retina, blocking checks for diabetic retinal disease.
Children and special cases:
- In children, even moderate blur can increase the risk of amblyopia (lazy eye), so treatment is initiated earlier.
- If you have other eye diseases (e.g., glaucoma, diabetes in the eye), earlier surgery may protect long-term vision.
H2: Treatment Options for Hypermature Cataract
Nowadays, various surgical and non-surgical treatment options are available for hypermature cataracts.
Surgical options for hypermature cataract treatment are as follows:
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE) / SICS:
It involves removing the entire lens through a single larger incision, often used for advanced cataracts or specific cases.
The more advanced phacoemulsification procedure has largely replaced this. This is a manual procedure and hence does not require any sophisticated infrastructure or technology.
- Phacoemulsification:
It utilizes ultrasound technology to break up and remove the clouded lens, requiring a small incision for faster recovery and minimal discomfort.
In it, the incision size is less than 1.8 mm, which reduces surgical invasiveness while simultaneously improving surgical outcomes.
Femto Bladeless Cataract Surgery utilizes advanced laser technology for precise incisions and lens fragmentation. Differing from traditional methods, its benefits include enhanced accuracy, quicker recovery, and reduced reliance on manual techniques.
Non-surgical Options:
- Medication: Although medication cannot reverse cataracts, it may be prescribed to manage associated symptoms such as inflammation or discomfort.
This may include anti-inflammatory eye drops or other medications to alleviate discomfort. Individuals with hypermature cataracts should consult an eye specialist to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to their specific condition.
H2: Complications of Hypermature Cataracts if Left Untreated
Leaving hypermature cataracts untreated for an extended period makes the condition grow severe with time.
- Glaucoma: Increased intraocular pressure from the cataract can lead to glaucoma, which damages the optic nerve.
- Blindness: Prolonged neglect of hypermature cataracts may ultimately lead to irreversible blindness.
- Secondary glaucoma: If fluid accumulation in the eye remains untreated, it can lead to secondary glaucoma.
- Inflammatory changes: Untreated cataracts may heighten the risk of inflammation and discomfort in the eyes.
- Compromised quality of life: Impaired daily activities and reduced independence due to compromised vision.
- Secondary infections: Increased susceptibility to eye infections due to untreated cataracts.
- Chronic pain and discomfort: Persistent eye pain and discomfort can be experienced without timely treatment.
- Functional limitations: Difficulty in driving, reading, and recognizing faces, limiting overall functionality.
- Complicated surgical intervention: Delayed treatment may require more complex surgical procedures to address advanced cataracts.
- Psychological impact: Untreated hypermature cataracts may lead to reduced self-esteem and increased stress, affecting mental well-being.
Post-Surgery Precautions for Hypermature Cataracts
Below are the post-surgery precautions for hypermature cataracts:
- Medication adherence for recovery: Adhere to the prescribed post-operative medication plan to facilitate a smooth recovery.
- Gentle eye care practices: Avoid rubbing and applying pressure to the eyes for improved healing after hypermature cataract surgery.
- Light shielding with sunglasses: Wear sunglasses outdoors to shield eyes from bright light during the crucial recovery phase.
- Activity moderation for eye strain prevention: Limit strenuous activities and heavy lifting to prevent eye strain during recovery.
- Scheduled follow-ups for monitoring: Attend scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any concerns closely.
- Hygiene measures for reduced infection risk: Maintain eye cleanliness and hygiene practices to minimize infection risks post-surgery.
- Immediate reporting of changes: Promptly report any unexpected vision changes or discomfort to your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Most cases of hypermature cataract result from a long-standing cataract that has progressed and now causes severe blurring and glare. Once daily life is affected or if red flags appear, timely surgery is the safest way to protect vision and eye health.
Non-surgical steps may help briefly, but they do not reverse the condition. With careful planning and follow-up, most people achieve clearer, more comfortable vision after treatment.
FAQs
What is a hypermature cataract?
A hypermature cataract is an advanced stage of cataract where the lens becomes very hard or starts to liquefy, causing severe blurring and an increased risk of complications.
What age group is more prone to hypermature cataracts?
Hypermature cataracts are more prevalent among individuals aged 60 and above. Regular eye examinations are vital in this demographic to detect and manage cataracts proactively.
How successful is the surgical removal of hypermature cataracts?
Surgical removal of a hypermature cataract is notably successful, demonstrating a high rate of effectiveness in restoring clear vision. Contemporary cataract surgery techniques, including advanced methods like phacoemulsification, ensure both safety and improved visual outcomes for individuals undergoing the procedure.
Can hypermature cataracts cause permanent vision loss?
Yes, hypermature cataracts can cause permanent vision loss if left untreated, as they may lead to high eye pressure or other complications.
How long does it take for hypermature cataracts to develop?
The development of hypermature cataracts can span several years and is influenced by factors like age, health, and genetics. Regular eye check-ups are crucial for early detection, allowing for timely intervention and proactive management.
Can hypermature cataracts be hereditary?
Yes, there is a hereditary component to hypermature cataracts. Genetic factors can contribute to an increased risk of developing cataracts. Individuals with a family history of cataracts should be vigilant and prioritize regular eye check-ups for early detection and management.
Can hypermature cataracts recur after surgical removal?
No, hypermature cataracts do not recur after lens removal; later blur can result from the capsule (PCO) and is usually treated with a quick laser procedure.