Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye. It is characterized by inflammation of the uvea, which can cause various symptoms and complications. In this guide, we will explore the uveitis symptoms, causes, and treatment options for uveitis.
Uveitis can affect people of all ages and can occur in one or both eyes. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any uveitis symptoms, as early diagnosis and uveitis treatment can help prevent complications and preserve your vision.
What Is Uveitis?
Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, which consists of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. The uvea is responsible for supplying blood to the retina and maintaining the overall health of the eye.
There are different types of uveitis, including anterior uveitis, intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, and panuveitis. The specific type of uveitis you have will determine the location of the inflammation within the eye.
Uveitis can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and injuries to the eye. It is important to understand the underlying uveitis cause in order to determine the most appropriate treatment.
What Causes Uveitis?
Uveitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections, such as viral, bacterial, or fungal infections
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Eye injuries or trauma
- Certain medications
- Inflammatory diseases, such as sarcoidosis or Crohn’s disease
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause of uveitis in your case.
Symptoms of Uveitis
The uveitis symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms of uveitis may include:
- Eye redness
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Blurred or decreased vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Floaters or spots in your vision
- Painful eye movements
If you experience any of these uveitis symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and uveitis treatment.
How Common Is Uveitis?
Uveitis is relatively uncommon, but it can affect people of all ages. It is estimated that uveitis affects approximately 1 in 4500 people. The condition can occur in both children and adults. While it can occur at any age, it is more commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 20 and 60. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any uveitis symptoms, regardless of your age.
Complications & Risk of Uveitis
If left untreated, uveitis can lead to various complications and potentially permanent vision loss. Some of the complications associated with uveitis include:
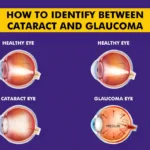
Cataracts: Uveitis can increase the risk of developing cataracts, which can cloud the lens of the eye and cause vision problems.
Glaucoma: Uveitis can increase the pressure inside the eye, leading to glaucoma, which can cause damage to the optic nerve and result in vision loss.
Macular edema: Uveitis can cause swelling in the macula, which is the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision.
Retinal detachment: Uveitis can increase the risk of retinal detachment, which occurs when the retina pulls away from the underlying tissue, leading to vision loss.
It is important to seek early diagnosis and treatment for uveitis to prevent these complications and preserve your vision.
You can read more about glaucoma surgery and cataracts surgery here.
How Is Uveitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing uveitis involves a comprehensive eye examination and medical history evaluation. Your healthcare professional may perform various tests, including:
- Visual acuity test
- Slit-lamp examination
- Intraocular pressure measurement
- Fundoscopy
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Uveitis Treatment Options
The uveitis treatment depends on the underlying uveitis cause and severity of the inflammation. It may include:
- Prescription eye drops or ointments to reduce inflammation
- Oral medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs
- Injections of medication into the eye
- Surgery, in severe cases or when complications arise
It is important to follow your healthcare professional’s recommendations for treatment and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor your condition.
Can Uveitis Be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of uveitis, there are some preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk:
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly
- Avoid self medication and consult an eye specialist
- Avoid eye injuries by wearing protective eyewear when necessary
- Manage underlying health conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, with the help of a healthcare professional
- Follow a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Attend regular eye examinations to detect any early signs of uveitis or other eye conditions
Why Choose Centre For Sight?
At Centre For Sight, we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of various eye conditions, including uveitis. Our team of experienced ophthalmologists and healthcare professionals are dedicated to providing personalized care and helping you preserve your vision.
We offer state-of-the-art facilities, advanced diagnostic tools, and a wide range of treatment options for uveitis. Whether you require medication, surgery, or ongoing management of your uveitis, we are here to support you every step of the way.
FAQs
What is uveitis?
Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye.
What are the symptoms of uveitis?
The uveitis symptoms may include eye redness, eye pain, blurred vision, sensitivity to light, floaters or spots in your vision, and painful eye movements.
How is uveitis diagnosed?
Uveitis is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination, medical history evaluation, and various tests, such as visual acuity test, slit-lamp examination, and blood tests.
Is uveitis contagious?
No, uveitis is not contagious.
What causes uveitis?
Uveitis can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, eye injuries, certain medications, and inflammatory diseases.
Can uveitis be cured?
While uveitis cannot always be cured, it can be managed and treated with appropriate medical intervention.
What does uveitis pain feel like?
Uveitis pain can vary from person to person, but it is often described as a sharp or throbbing pain in the affected eye along with intolerance to bright light.