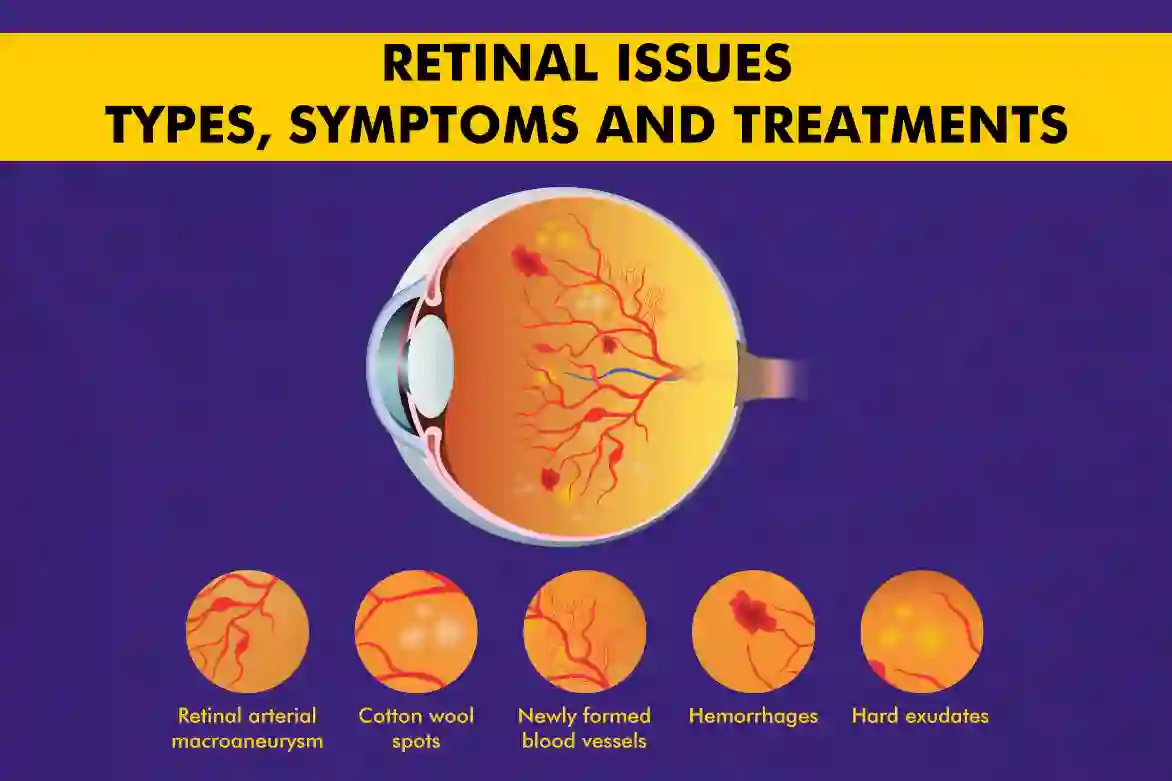
Summary: Retinal issues, if untreated, may cause irreversible vision loss. Early diagnosis, advanced treatments, lifestyle management, and regular eye checkups greatly improve outcomes, highlighting the need for proactive retinal healthcare.
|
Key Takeaways:
|
The retina is a delicate and essential part of the eye. It is a thin layer of tissue located at the back of the eye that plays a crucial role in vision. The retina contains specialized cells called photoreceptors that detect light and send signals to the brain, allowing us to see. Unfortunately, the retina can be susceptible to various issues that can cause eye problems, affect our vision and overall eye health.
What Are the Common Retinal Diseases?
There are several common retinal issues that individuals may encounter. These include:
- Retinal detachment: This occurs when the retina separates from the underlying tissue, leading to vision loss in the affected area.
- Macular degeneration: This is a progressive condition that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision.
- Diabetic retinopathy: People with diabetes may develop this condition, which is characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
- Retinal tears: These are small breaks in the retina that can occur due to trauma or other underlying conditions.
These are just a few examples of common retinal issues, and each condition may have its own unique causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors of Eye Problems
Several factors can contribute to various eye problems, especially the development of retinal issues. These include:
- Age: As we get older, the risk of certain retinal conditions, such as macular degeneration, increases.
- Genetics: Some retinal disorders have a genetic component, meaning they can be passed down through families.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing retinal issues.
- Eye trauma: Injuries to the eye can cause retinal tears or detachments.
- Smoking: Tobacco use has been linked to an increased risk of retinal problems.
Understanding these causes and risk factors of retinal issues can help individuals take preventive measures and seek early treatment if necessary.
Symptoms of Retinal Diseases
The symptoms of retinal issues can vary depending on the specific condition. However, some common signs to watch out for include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Floaters or dark spots in the field of vision
- Flashes of light
- Difficulty seeing in low light or at night
- Loss of peripheral vision
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye examination.
Types of Retinal Diseases
Various types of retinal diseases can impact vision. Some of the most common ones include:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): This is the leading cause of vision loss in individuals over the age of 50. It affects the macula, leading to a gradual loss of central vision.
- Diabetic retinopathy: As mentioned earlier, this condition occurs in individuals with diabetes and can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
- Retinal vein occlusion: This occurs when a blood vessel in the retina becomes blocked, leading to vision loss in the affected area.
- Retinitis pigmentosa: This is a group of genetic disorders that cause a gradual loss of vision due to the breakdown and loss of cells in the retina.
These are just a few examples of retinal diseases, and each condition may require different treatment approaches.
How Experts Confirm Retinal Conditions (Diagnosis)
An ophthalmologist may dilate the pupils and perform imaging tests, such as OCT, angiography, or ultrasound. These tools help detect common retinal problems such as tears, swelling, bleeding, or detachment, ensuring accurate diagnosis and timely care.
Treatment Options for Retinal Disorders
The treatment options for retinal disorders can vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage the underlying cause of the retinal issue or to slow down its progression.
- Laser therapy: This involves using a laser to seal leaking blood vessels, treat retinal tears, or destroy abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
- Vitrectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the gel-like substance (vitreous) from the center of the eye to treat conditions like retinal detachment or macular holes.
- Intraocular injections: Medications can be injected directly into the eye to target specific retinal conditions, such as age-related macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy. Anti VEGF injections are most commonly used among all.
It’s important to consult with an ophthalmologist or retina specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment option for your retinal issues.
Preventing Retinal Issues
While not all retinal issues can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk or delay the progression of certain conditions. Some preventive measures include:
- Regular eye exams: Routine eye examinations can help detect any early signs of retinal issues and allow for timely intervention.
- Managing chronic diseases: Proper management of conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can help reduce the risk of developing retinal diseases.
- Protecting your eyes: Wearing protective eyewear during activities that pose a risk of eye injury can help prevent retinal tears or detachments.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, not smoking, and protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays can all contribute to better retinal health.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can take an active role in maintaining their retinal health.
FAQs
What are the most common causes of retinal detachment?
Retinal detachment often results from retinal tears, severe eye injury, aging, diabetes-related changes, or extreme nearsightedness that weakens the retina.
What are the signs of retinal damage?
Key signs include sudden floaters, flashes of light, blurred vision, loss of side vision, and a shadow or curtain effect across the eye.
What is the treatment for a detached retina in humans?
Treatment usually involves surgery, such as vitrectomy, pneumatic retinopexy, or scleral buckle, to reattach the retina and prevent permanent vision loss.
What are the symptoms of a retinal problem?
Symptoms can include sudden flashes of light, floaters, blurry vision, or a shadow or curtain in your field of vision.
Can retina problems be cured?
Treatment options exist depending on the condition, ranging from medication to surgery. Some conditions can be managed effectively.
What is the most common retinal disease?
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common retinal disease.
How to improve retina?
Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, protecting your eyes from UV rays, and regular eye exams can help maintain retinal health.
Can the retina repair itself?
In some cases, the retina can heal itself, especially if the damage is minor. However, severe damage often requires medical intervention.
Which fruit is best for the retina?
Fruits high in antioxidants like berries (blueberries, strawberries) and citrus fruits (oranges, lemons) are beneficial for retinal health.