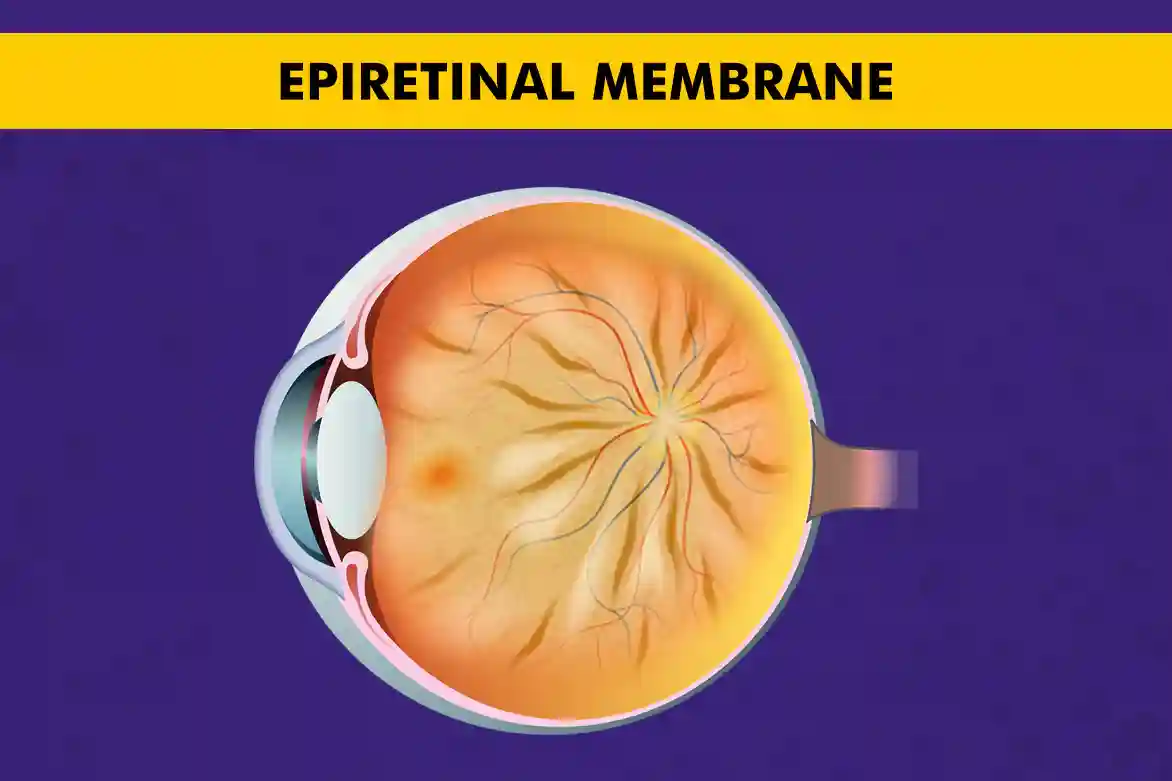
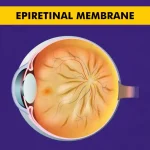
An epiretinal membrane (ERM), also known as macular pucker or cellophane maculopathy, is a thin layer of scar tissue that forms on the surface of the retina. This condition can cause a range of visual symptoms and may require treatment to improve vision.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and epiretinal membrane treatment, providing you with the information you need to understand and manage this condition.
What Is Epiretinal Membrane?
To understand epiretinal membrane, it is important to first have a basic understanding of the structure of the eye. The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye and is responsible for converting light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The macula is the central part of the retina and is responsible for sharp, detailed vision.
An epiretinal membrane forms when cells from the vitreous gel, a gel-like substance that fills the inside of the eye, migrate onto the surface of the retina. These cells can then proliferate and create a thin layer of scar tissue, which can distort the macula and affect vision.
Causes of Epiretinal Membrane
The exact cause of epiretinal membrane formation is not always clear. However, there are several factors that may contribute to its development. These include:
- Age: Epiretinal membranes are more common in older adults, with the risk increasing with age.
- Eye conditions: Certain eye conditions, such as retinal tears, retinal detachments, and inflammation, can increase the risk of developing an epiretinal membrane.
- Eye surgeries: Previous eye surgeries, such as cataract surgery or retinal detachment repair, can increase the risk of developing an epiretinal membrane.
- Trauma: Eye trauma or injury can sometimes lead to the formation of an epiretinal membrane.
It is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop an epiretinal membrane, and the condition can also occur in individuals with no known risk factors.
Symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane
Epiretinal membranes can cause a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision: Vision may appear blurry or distorted, with straight lines appearing wavy or bent.
- Decreased central vision: The central vision, which is responsible for detailed tasks such as reading or recognizing faces, may be affected.
- Floaters: Floaters are small specks or spots that float across the field of vision.
- Difficulty seeing fine details: Fine details, such as small print or facial features, may be harder to see.
- Color distortion: Colors may appear faded or less vibrant.
It is important to note that not everyone with an epiretinal membrane will experience symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary.
How Is Epiretinal Membrane Diagnosed?
If you are experiencing symptoms of an epiretinal membrane, it is important to see an eye care professional for a comprehensive eye examination. During the examination, your eye care professional may perform the following tests:
- Visual acuity test: This test measures how well you can see at various distances.
- Dilated eye examination: Your eye care professional will use special eye drops to dilate your pupils and examine the retina and macula.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): This imaging test provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing your eye care professional to assess the thickness and characteristics of the epiretinal membrane.
Based on the results of these tests, your eye care professional can diagnose an epiretinal membrane and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Epiretinal Membrane Treatment
The treatment for an epiretinal membrane depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on vision. In some cases, if the membrane is not causing significant vision problems, no treatment may be necessary. However, if the symptoms are affecting daily activities or quality of life, epiretinal membrane treatment options may include:
- Observation: If the symptoms are mild and not significantly impacting vision, your eye care professional may recommend regular monitoring without any specific intervention.
- Vitrectomy surgery: This surgical procedure involves the removal of the vitreous gel and the epiretinal membrane. It is typically performed under local anesthesia and can help improve vision in many cases.
- Medications: In some cases, your eye care professional may recommend medications, such as corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation and swelling associated with the epiretinal membrane.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the impact on vision, and individual patient preferences. Your eye care professional will work with you to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Risk Factors of Epiretinal Membrane
While the exact cause of epiretinal membrane formation is not fully understood, there are several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing the condition. These include:
- Age: Epiretinal membranes are more common in older adults, with the risk increasing with age.
- Eye conditions: Certain eye conditions, such as retinal tears, retinal detachments, and inflammation, can increase the risk of developing an epiretinal membrane.
- Eye surgeries: Previous eye surgeries, such as cataract surgery or retinal detachment repair, can increase the risk of developing an epiretinal membrane.
- Trauma: Eye trauma or injury can sometimes lead to the formation of an epiretinal membrane.
It is important to note that having these risk factors does not guarantee the development of an epiretinal membrane, and the condition can also occur in individuals with no known risk factors.
Prevention and Management
Unfortunately, there are no known ways to prevent the development of an epiretinal membrane. However, there are several steps you can take to manage the condition and reduce the impact on vision:
- Regular eye exams: Routine eye exams can help detect any changes in the retina and macula, allowing for early intervention if necessary.
- Healthy lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help maintain overall eye health.
- Protect your eyes: Taking precautions to protect your eyes from trauma or injury can help reduce the risk of developing an epiretinal membrane.
- Follow your eye care professional’s recommendations: It is important to follow your eye care professional’s recommendations for monitoring and managing your epiretinal membrane.
By following these steps, you can take an active role in managing your condition and optimizing your vision.
Conclusion
Epiretinal membrane is a condition that can affect the macula, causing symptoms such as blurred or distorted vision. While the exact cause is not always clear, there are several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing an epiretinal membrane. Fortunately, there are treatment options available to improve vision and manage the condition. Remember, early detection and timely intervention can make a significant difference in preserving and optimizing your vision. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, you can maintain good eye health and ensure the best possible outcomes.
FAQs
How serious is the epiretinal membrane?
The severity of an epiretinal membrane can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that do not significantly impact vision, while others may have more severe symptoms that affect daily activities.
What is the treatment for epiretinal membranes?
The treatment for epiretinal membranes depends on the severity of symptoms and the impact on vision. If the symptoms are affecting daily activities or quality of life, treatment options may include observation, vitrectomy surgery, or medications.
What happens if the epiretinal membrane is not removed?
Leaving the epiretinal membrane untreated may result in persistent or worsening symptoms.
What is the success rate of epiretinal membrane surgery?
The success rate of epiretinal membrane surgery is high but can vary depending on various factors, including the severity of the membrane, the individual’s overall eye health, and the skill of the surgeon.
Is epiretinal membrane surgery painful?
Epiretinal membrane surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, so the procedure itself is not painful. However, some discomfort or mild soreness may be experienced after the surgery.
Can glasses correct the epiretinal membrane?
Glasses alone cannot correct the visual distortions caused by an epiretinal membrane. However, in some cases, glasses may help optimize vision by providing sharper focus or reducing other refractive errors.